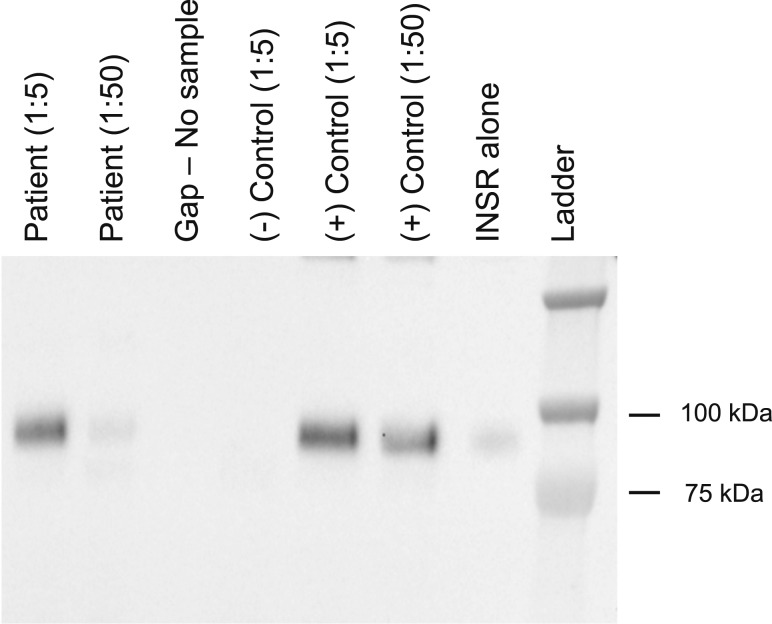
Figure 1.
Anti-insulin receptor autoantibody assay. Anti-insulin receptor autoantibodies are demonstrated by immunoprecipitation of solubilized insulin receptors with, from left to right: the patient’s serum at 1:5 and 1:50 dilutions, compared with negative (1:5 dilution) and positive (1:5 and 1:50 dilutions) controls, and the INSR alone (10). For detection of endogenous anti-insulin receptor antibodies, serum was first diluted 1 in 5 or 1 in 50 in phosphate-buffered saline prior to incubation with an optimized concentration of a crude preparation of recombinant human INSR (hINSR; a lysate of CHO cells stably expressing human insulin receptor) in immunoprecipitation buffer (2.52 g/L NaF, 8.92 g/L Na4P2O7, 100 mM HEPES, and 300 mM NaCl) for 4 hours at 2°C to 8°C with gentle agitation. Antibodies were then captured using goat antihuman IgG agarose beads (A3316, Sigma, Billerica, MA; 2 hours at 2-8°C with gentle agitation). Unbound hINSR was washed away with bead wash buffer (immunoprecipitation buffer as previously mentioned with the addition of 10 mM EDTA, pH 8.0, and 0.2% Triton-X 100) before reducing and fragmenting captured hINSR using Laemmli buffer. Samples were resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on 8% Bis-Tris gels before detection of hINSR beta subunit using hINSR beta subunit-specific antibody (sc-711; Santa Cruz, Dallas, TX) by immunoblotting. INSR, insulin receptor.