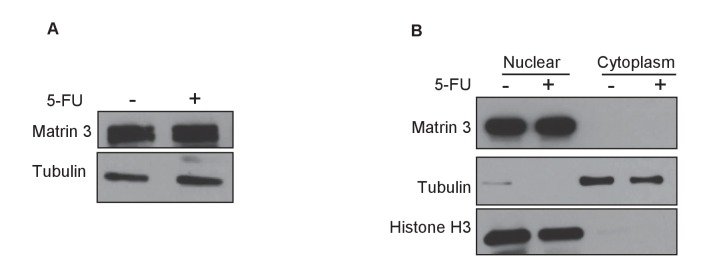
Figure 5. Matrin 3 binds to PINCR and functions as a downstream effector of PINCR.
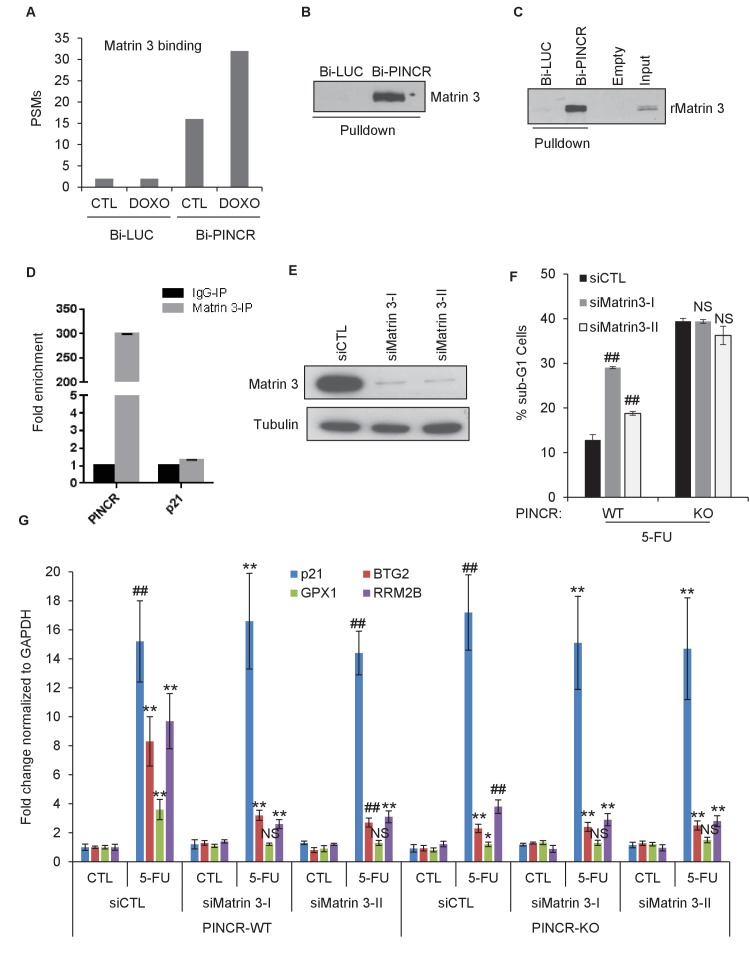
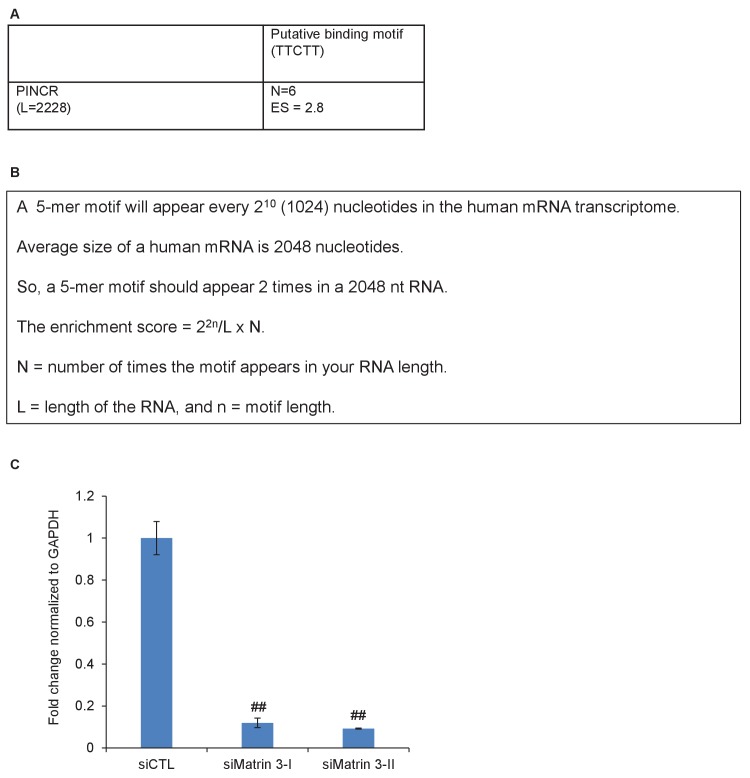
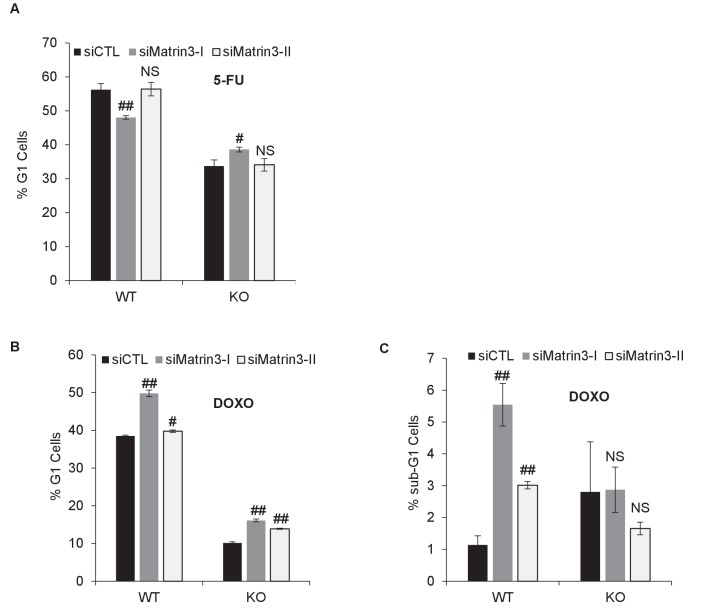
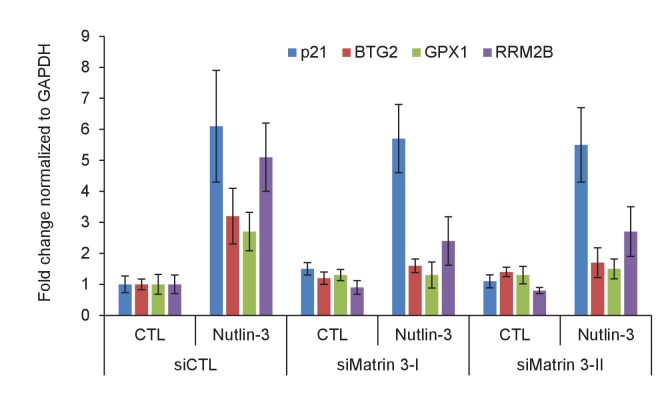
(A) Peptide spectrum matches (PSMs) corresponding to Matrin 3 in the Bi-LUC and Bi-PINCR pulldowns from mass spectrometry analysis. (B, C) Streptavidin pulldowns followed by immunoblotting was performed following incubation of Bi-LUC and Bi-PINCR RNA with DOXO-treated HCT116 nuclear extracts (B) or recombinant Matrin 3 (rMatrin 3) (C). (D) Specific enrichment of PINCR in the Matrin 3 IPs was assessed by qRT-PCR from 24 hr 5-FU-treated formaldehyde cross-linked HCT116 cells. p21 mRNA was used as negative control. (E) PINCR-WT cells were transfected with CTL or two independent Matrin 3 siRNAs (I and II) for 48 hr and Matrin 3 knockdown was measured by immunoblotting. (F) PINCR-WT and PINCR-KO cells were transfected with CTL or Matrin 3 siRNAs and after 48 hr the cells were untreated or treated with 5-FU for 48 hr. The effect on the sub-G1 population was assessed by PI staining followed by FACS. (G) PINCR-WT and PINCR-KO cells were transfected with CTL or Matrin 3 siRNAs for 48 hr; transfected cells were left untreated or treated with 5-FU for 24 hr and qRT-PCR was performed. Error bars in D, F and G represent SD from three independent experiments. *p<0.05; #p<0.01; **p<0.005.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.23244.038