Figure 3. Construction of KSHV gB-F and characterization of KSHV gB VLPs.
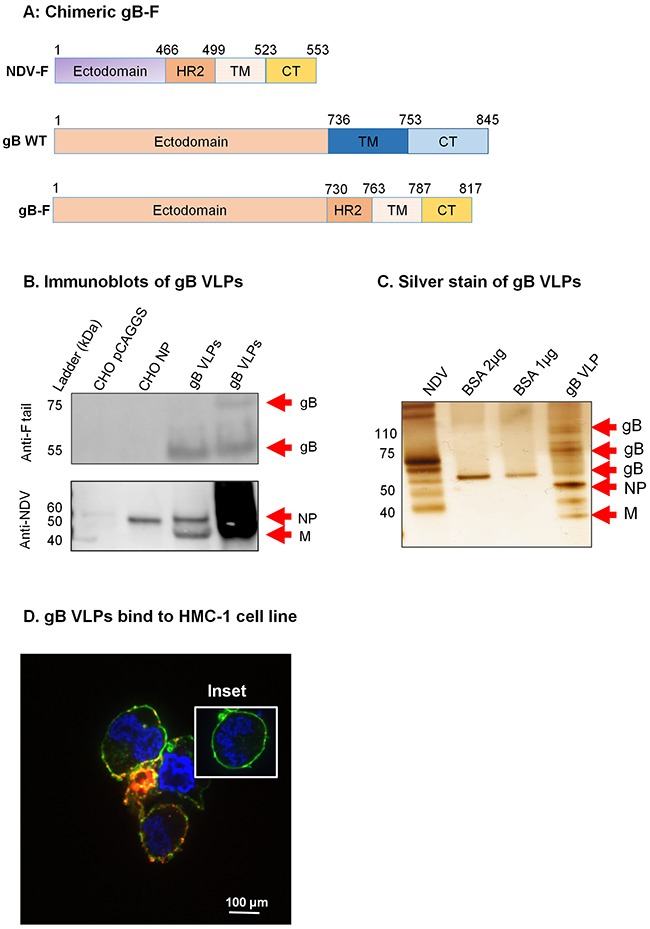
A. KSHV gB-F plasmid constructs (not to scale) showing full-length NDV-F (top), full-length/wild-type (WT) gB (middle), and chimeric gB-F (bottom). B. CHO cells transfected with empty pCAGGS vector or pCAGGS-NP, or purified gB VLPs were lysed and analyzed by immunoblot using polyclonal anti-NDV F tail and anti-NDV. Anti-F tail (top panel) detected the cleaved forms of the gB-F fusion protein (˜55 and ˜75 kDa) in 5 μg and 10 μg of purified gB VLPs (lanes 3-4), but not in CHO pCAGGS or CHO NP lysates (negative controls, lanes 1-2). Anti-NDV (bottom panel) detected NP alone in CHO NP (positive control, lane 2), and NP and M in gB VLPs (lanes 3-4), but not in CHO pCAGGS (negative control, lane 1). C. Silver stain was used to visualize VLP purity relative to purified NDV, and detected uncleaved and cleaved gB-F proteins of ˜110, and 55-75 kDa. Arrows indicate viral/VLP components in 5 μl purified NDV diluted 1:30 (lane 1), and 1 μl purified gB VLPs diluted 1:40 (lane 4). Lanes 2 and 3 were loaded with 1 μg and 2 μg BSA, respectively for protein quantification. D. Confocal microscopy shows gB VLPs binding to surface receptors on HMC-1 cells. Purified gB VLPs were incubated with HMC-1 cells for 10 min at room temperature and stained with rabbit polyclonal anti-gB, followed by secondary antibody conjugated with Alexa-Fluor 594 (red) to detect gB VLPs, cholera toxin (green) to detect lipid rafts, and DAPI (blue) to detect HMC-1 nuclei. The red and green staining shows VLPs bound cell membranes; HMC-1 cells not incubated with VLPs did not stain red (negative control, inset).
