Figure 2. Transplantation of BCR-ABL expressing BM cells influences the immunophenotype of the recipient mice and the dasatinib effect.
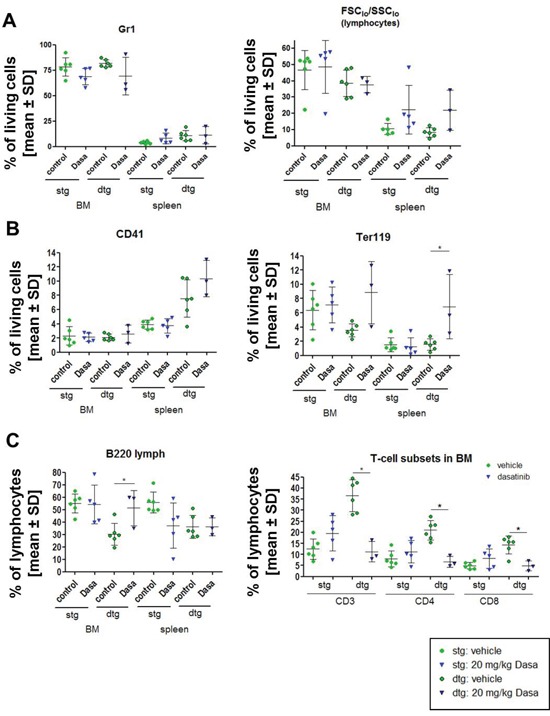
The expression of BCR-ABL was induced in double transgenic (dtg) donor animals and pooled for transplantation of 1×106 BM cells in comparison to BM of SCLtTA single transgenic (stg) control mice. (A) After 15 weeks of induction, the mice were treated for 9 days with control vehicle (green circles) or 20 mg/kg dasatinib (blue triangle) (control: stg/dtg: n = 6/6; dasatinib stg/dtg: n = 5/3). Depicted are the percentages of Gr1 positive granulocytic cells and FCSlow/SSClow (lymphocytes) gated on living cells in the BM and the spleen of stg in comparison to dtg mice after dasatinib treatment. (B) Analysis of the percentage of CD41 positive megakaryocytes and Ter119 positive erythroid cells in BM and spleen of vehicle and dasatinib treated mice, gated on all living cells. (C) Percentage of B220+ lymphocytes was evaluated in BM and spleen. Distribution of T cells (CD3, CD4, CD8) in the BM of stg and dtg control or dasatinib treated mice (gated for % of FCSlow/SSClow (lymphocytes)). All data are shown as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05.
