Figure 3.
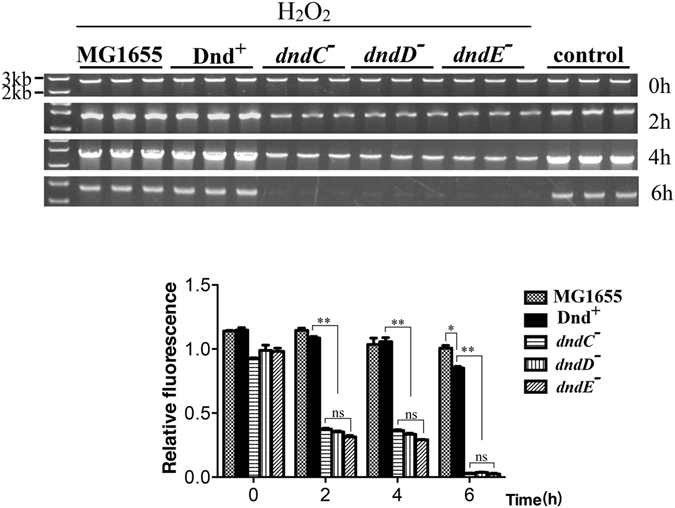
DNA phosphorothioation protects Hpx- cells from oxidative damage to genomic DNA. MG1655 and Hpx−/Dnd cells were treated with 1 mM H2O2. The reaction was stopped at 2-hour intervals by adding catalase, and total genomic DNA was isolated and subjected to polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification to obtain a 2.7 kb DNA fragment. PCR was performed using equivalent amounts of template DNA for each reaction mixture. The PCR products were fractionated and scanned on an agarose gel to assess DNA oxidative damage. The loading quantities of PCR products were adjusted properly in order to observe the bands of Hpx−/dnd mutants, and the amounts of DNA were normalized to that of the untreated control (Hpx−). Values are the means and standard deviations from three experiments. The data were analyzed by Student’s t test. **P < 0.01; ns, not significantly different. Full-length gels are included in Supplementary Figure 9.
