Figure 1.
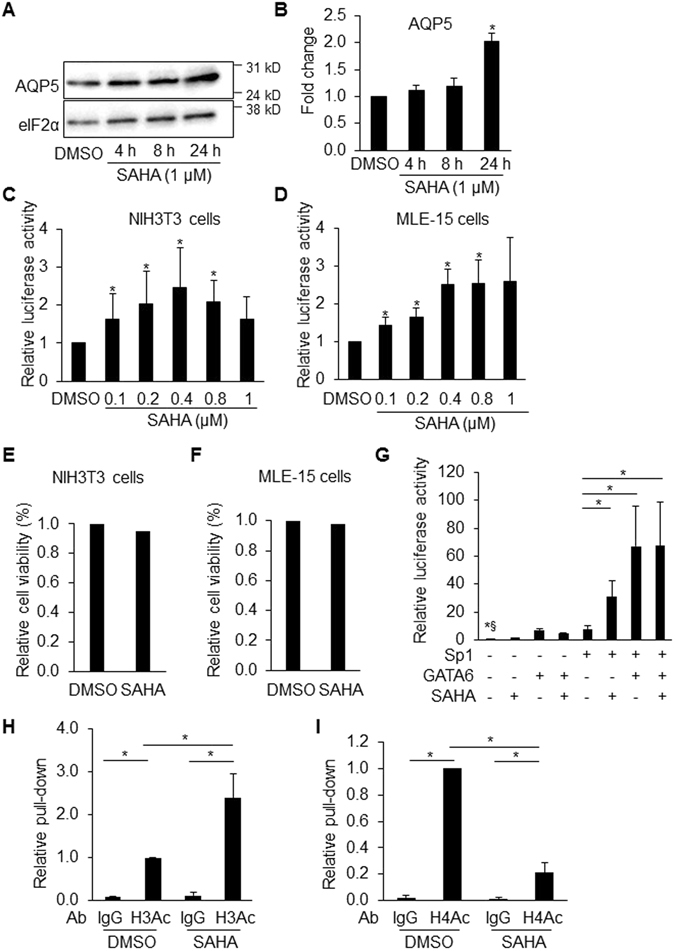
HDAC inhibitor increases AQP5 expression. Representative western blot (WB) (A) and corresponding quantitative analysis (B) shows that treatment of MLE-15 cells with HDAC inhibitor SAHA for 24 h increases AQP5 (27 kD) protein expression (normalized to eIF-2α (36 kD)) (n = 4, *p < 0.05 compared to DMSO). SAHA increases Aqp5 luciferase activity in a dose-dependent manner in both NIH3T3 (C) and MLE-15 cells (D) transfected with -358-Aqp5-Luc following 18 h treatment. Protein concentrations were used for sample normalization (n = 3, *p < 0.05 compared to DMSO). Twenty-four h of SAHA (1 µM) treatment had no cytotoxic effects on NIH3T3 (E) and MLE-15 cells (F). (G) GATA6 (pCDNA3/GATA6), Sp1 (pCMV/Sp1) and their corresponding empty vectors were transfected individually or in combination into NIH3T3 cells, followed by treatment with SAHA (0.8 µM) for 18 h. SAHA significantly increases Sp1-activated -358 Aqp5 promoter/enhancer activity. Protein concentrations were used for sample normalization. n = 3 except for column 2 (empty vectors with SAHA), where n = 2, *§p < 0.05 shows significant difference between control (column 1, empty vectors with DMSO) and all other groups except column 2. Since column 2 is only n = 2, we did not perform statistical analysis for comparison with control. *p < 0.05 compared to column 5 (Sp1 with DMSO). ChIP with anti-acetyl-H3 (H3Ac) and anti-acetyl-H4 (H4Ac) Abs demonstrates enrichment of H3 acetylation (H) and decreased H4 acetylation (I) at the Aqp5 promoter/enhancer region homologous to the proximal 358-bp of the rat Aqp5 promoter following SAHA treatment (1 µM, 24 h) in MLE-15 cells (n = 3, *p < 0.05). ChIP efficiency was calculated relative to untreated cells precipitated with H3Ac and H4Ac Ab, respectively, which was set as 1. Rabbit IgG pull-down is used as control.
