Figure 2.
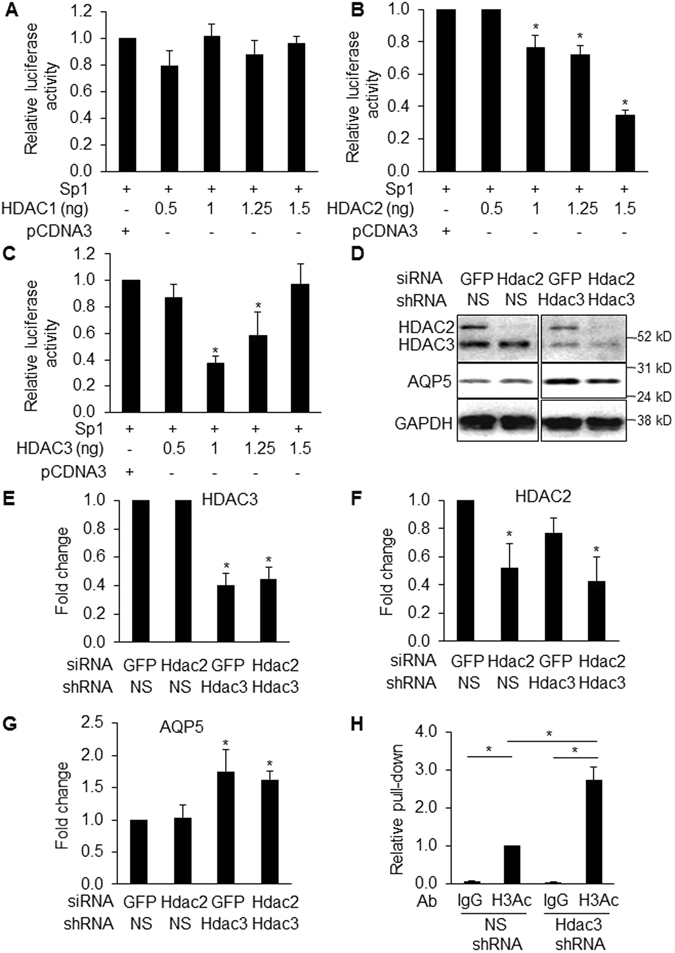
HDAC3 modulates expression of AQP5. NIH3T3 cells were co-transfected with 358-Aqp5-Luc, Sp1 and increasing amounts of HDAC1 (A), HDAC2 (B) and HDAC3 (C) expression vectors or empty vector (pCDNA3). HDAC2 and HDAC3, but not HDAC1 inhibited Sp1-activated Aqp5 transcription. Protein concentrations were used for sample normalization (n = 3, *p < 0.05 compared to empty vector). WB (D) and corresponding quantitative analysis (E–G) show that AQP5 expression (normalized to GAPDH (37 kD)) is significantly upregulated (D,G) following knockdown of HDAC3 (59 kD) with shRNA (D,E) but not HDAC2 (49 kD) with siRNA (D,F) (n = 3, *p < 0.05 compared to non-silencing shRNA and GFP siRNA) in MLE-15 cells. (H) ChIP with anti-acetyl-H3 Ab (H3Ac) demonstrates enrichment of H3 acetylation at the Aqp5 promoter/enhancer region homologous to the proximal 358-bp of the rat Aqp5 promoter following HDAC3 knockdown in MLE-15 cells (n = 3, *p < 0.05). ChIP efficiency was calculated relative to non-silencing shRNA (NS-shRNA)-treated cells precipitated with H3Ac Ab, which was set as 1. Rabbit IgG pull-down is used as control.
