Figure 1.
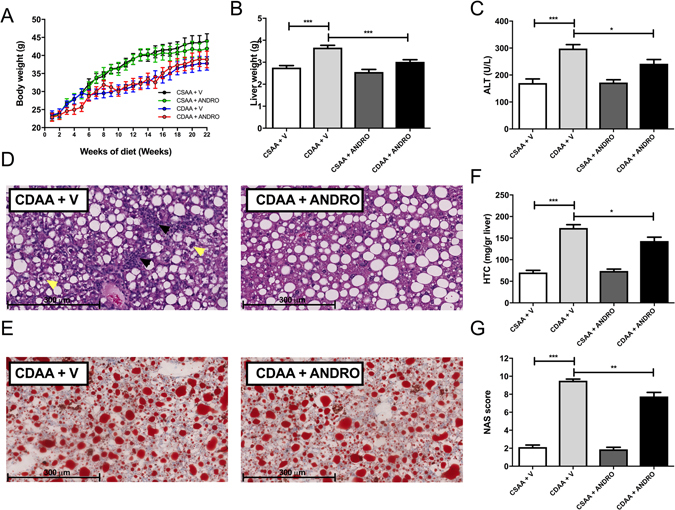
Andrographolide-treated mice are protected from CDAA-induced hepatomegaly and liver injury. Mice weaned after 21 days were placed on normal chow diet for 4 weeks and thereafter placed either on choline-deficient amino acid-defined (CDAA) or choline-supplemented L-amino acid defined (CSAA) diets for an additional 22 weeks. During this period mice were injected with AP three times per week (1 mg/kg, intraperitoneally). (A) Body weight gain, (B) Liver weight, (C) alanine aminotransferase (ALT) serum levels, (D) Histological evaluation of liver tissue (hematoxylin/eosin staining), inflammatory foci and hepatocyte ballooning are indicated by black and yellow arrows respectively. (E) Hepatic triglyceride content (HTC). (F) Oil-red-O staining of liver samples. (G) Non-alcoholic activity score (NAS) as assessed by a pathologist in a blindly fashion. Data are shown as means ± SEM. Statistical significance was evaluated using ANOVA with a post-hoc Bonferroni multiple-comparison test (*p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01 and ***p ≤ 0.001).
