Figure 3.
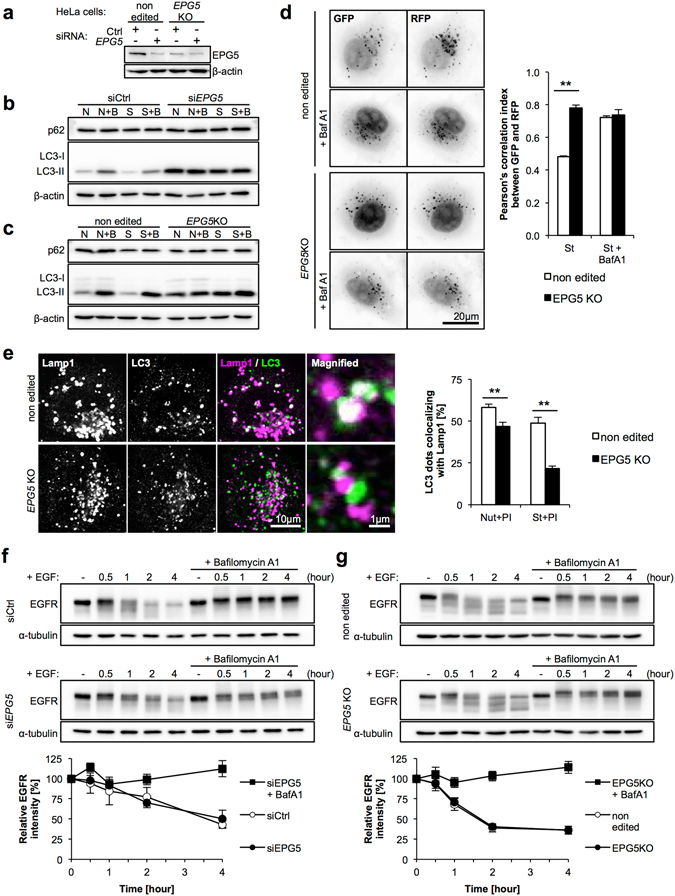
Autophagic impairment is caused by reduced fusion between autophagosomes and lysosomes in EPG5 KD and KO cells. (a) EPG5 depletion by siRNA treatment. (b,c) LC3-II has accumulated and autophagic flux is stopped in EPG5 KD and KO HeLa cells. (d) Tandem fluorescent-tagged LC3 (tf-LC3) assay indicated reduced autophagosome-lysosome fusion. EPG5 KO cells were infected with a retroviral mRFP-GFP-LC3 construct, then incubated in nutrient-rich or starved media with/without BafA1 for two hours. BafA1 inhibited lysosomal V-ATPase and led to disruption of the lysosomal acidic environment, as well as inhibition of autophagosome-lysosome fusion, which we used as the negative control for this experiment. RFP and GFP fluorescence images were obtained, and Pearson’s correlation index was calculated to show colocalization between RFP and GFP. Higher colocalization indicates accumulation of autophagosomes. (e) Colocalization of punctate LC3 staining with Lamp1 in the presence of protease inhibitors was lower in EPG5 KO cells under both nutrient rich and starved conditions. (f,g) Endocytic degradation of EGFR was normal in EPG5 KD and KO cells. N or Nut, nutrient-rich conditions; S or St, starved conditions; B or BafA1, Bafilomycin A1; PI, protease inhibitors (E64d+ pepstatin A). The mean and SD are from at least three independent experiments, with 10 images assessed per treatment condition. Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed Student’s t-test; **p < 0.01.
