Fig. 3.
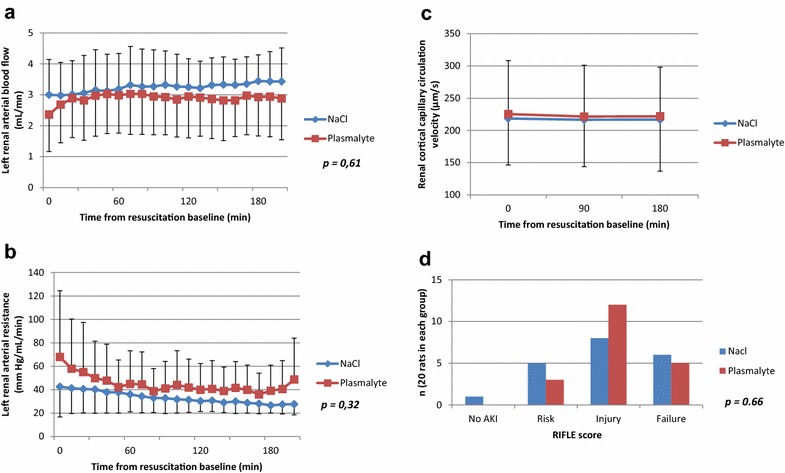
Renal hemodynamic and renal function during resuscitation. All data are presented as mean and standard deviation; p values were obtained using a mixed linear regression model for a and b and using the Mann–Whitney test for c and d. There was no significant difference between the two groups in the left arterial renal rate measured by TTU probes (a), left renal arterial resistance (b) and renal cortical capillary velocity (c) measured by Side Dark Field Camera (p = 0.41 at resuscitation baseline time, p = 0.54 at 90 min after resuscitation baseline and p = 0.51 at 180 min after resuscitation baseline). Distribution in the RIFLE classification (d) (based on creatinine plasma concentration, inulin clearance and creatinine clearance) was similar in both groups as shown in a (p = 0.66 for all classes, p = 0.34 for RIFLE score 0, p = 0.44 for RIFLE score 1, p = 0.22 for RIFLE score 2 and p = 0.74 for RIFLE score 3)
