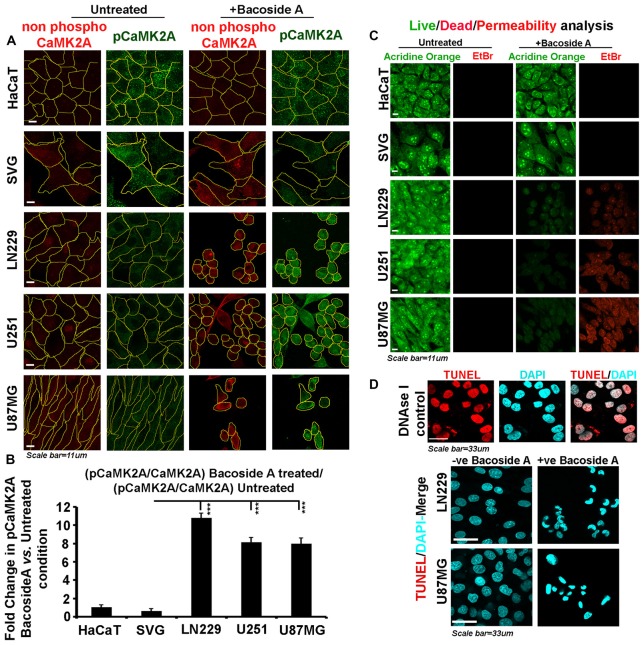
Figure 9.
Bacoside A activates extensive T286 phosphorylation of CaMK2A and non-apoptotic glioblastoma cell death. (A) Single cell quantitative image analysis procedure (see John et al., 2017) was employed to measure non-phospho CaMK2A and phospho CAMK2A T286 protein levels in normal human cells: SVG-subventricular zone derived glial cells; HaCaT-epidermal keratinocytes and in various GBM patient derived tumor cell lines: U87MG, U251 and LN229 upon Bacoside A (8 μg/ml) treatment for 24 h. (B) The proportion of phosphorylated CaMK2A determined by normalizing average signal of pCaMK2A-T286 to average signal from non-phospho CaMK2A in BM treated cells vs. the ratio in the normal cells, showed higher levels of pCaMK2A in treated tumor cells but not the normal control cell lines. Please note that just “CaMK2A” in the formula refers to predominantly the non-phosphorylated pool. The analysis is representative of three independent experiments and in each experiment protein signal was quantified from over 200 cells in five random fields. (C) Acridine orange (green, live cell marker probe)/EtBr (red, damaged and dead cell marker dye) based cytotoxicity and viability analysis over 24 h post Bacoside A treatment at 8 μg/ml showed specific cytotoxic effects on LN229/U87MG/U251 glioblastoma cell lines vs. the normal cells. (D) LN229 and U87MG GC treated with 8 μg/ml of Bacoside A for 48 h were negative for TUNEL staining (indicator assay for apoptotic cell death). ***p < 0.001. Error bar = SD The analysis is representative of three independent experiments.