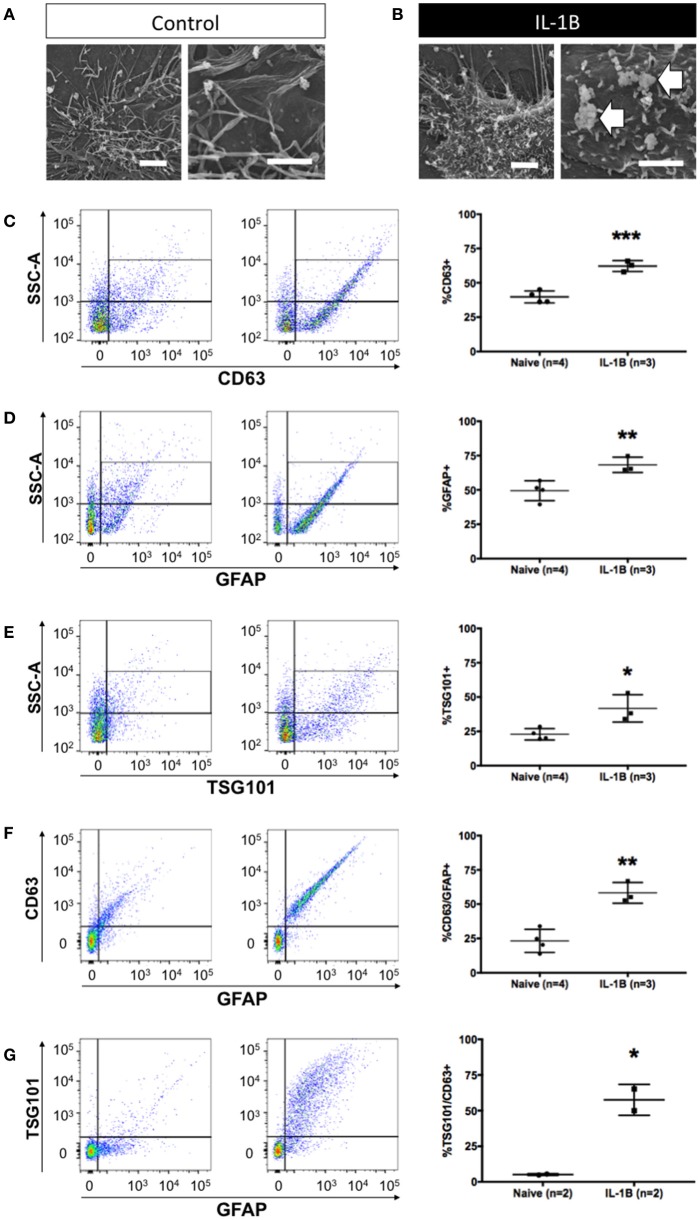
Figure 2.
Quantitative increase in detection of astrocytic exosomes media from primary astrocyte cultures following treatment with IL-1β. Scanning electron micrographs of astrocytes under control conditions (A) and after 1 h after IL-1B-stimulation (B). Magnifications in A&B are: 6,500x, left panel, and 10,000x, right panel). Note (arrows) the membrane perturbations resulting from cytokine stimulation that have been associated with process of extracellular vesicle release (B). (C–G) Analysis of astrocyte-derived exosomes from primary glial cultures using flow cytometry using antibodies against CD63 (C), GFAP (D), and Tsg101 (E) show elevated detection of events (exosomes) following IL-1B treatment. Additional analyses of GFAP+/CD63+ (F) and GFAP+/Tsg101+ (G) labeling confirmed an increased relative abundance of astrocyte-derived (GFAP+) exosomes (CD63+ or Tsg101+). Control (vehicle) treated cultures (“Naive”) had an identifiable amount of exosomes in conditioned media but the proportion of exosomes detected was markedly increased in response to IL-1β treatment. Significance is indicated where: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 t-test. Scale bars in (A,B) = 1 μm.