Figure 2. Cardiac cell‐to‐cell transfer of non‐coding RNAs.
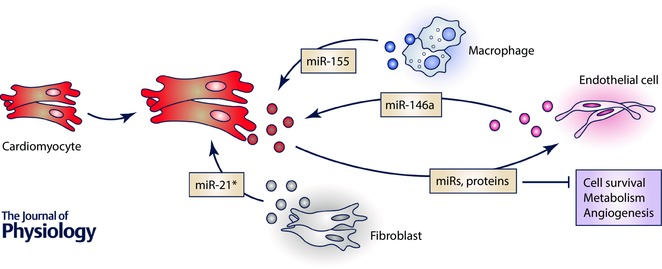
In general cells communicate with each other to create distinct microenvironments and share resources. Cardiac cells, including cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial and immune cells, also communicate with each other by means of extracellular vesicles, namely exosomes (represented by dots in different colours, depending on cell source). Cardiomyocytes are known to directly transfer exosome cargo to endothelial cells and thereby alter several basic cellular functions on the recipient cells such as cell cycle, metabolism and angiogenesis. To date, a very limited number of studies have mainly focused on identifying the content of exosomes that are transferred from other cell types (endothelial cells, fibroblasts and macrophages) into cardiomyocytes and how this cargo interferes with cardiomyocyte behaviour and, subsequently, cardiac remodelling.
