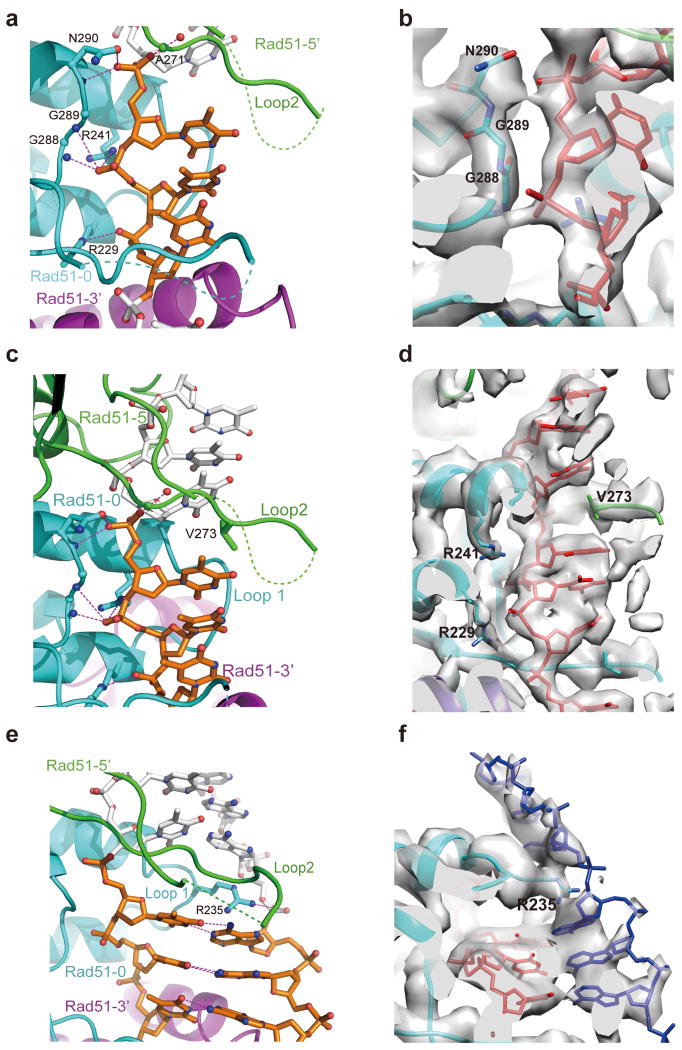
Figure 3. Interaction of RAD51 with DNA in the presynaptic and post-synaptic complexes.
(a) In the presynaptic complex, each nucleotide triplet connects with three RAD51 protomers that are shown in green, cyan and purple following the direction from 5′ to 3′. (b) The EM density in corresponding view of (a) showing that ssDNA interacts with three RAD51 residues that are conserved in RecA. DNA is in red color. (c) The adjacent triplets in a presynaptic complex are separated and stabilized by V273 in Loop 2 of the middle RAD51. RAD51 mainly interacts with the backbone of ssDNA from the front view. (d) The EM density in corresponding view of (c) showing the interaction between V273 and ssDNA. DNA is in red color. (e) The complementary strand in the post-synaptic complex is observed in a similar extended state with ssDNA. R235 in Loop 1 facilitates the separation of the neighboring triplets from the back view of (b). Key residues are labeled with the potential hydrogen bonds highlighted. (f) The EM density in the corresponding view of (e) showing the interaction of R235 and the complementary strand in blue color. The EM density is shown at a high threshold so the complementary strand phosphate backbone is relatively weak. The invading strand is in red color.