Abstract
Background
Viruses interact with host cellular factors to construct a more favourable environment for their efficient replication. Expression of cyclophilin B (CypB), a cellular peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase), was found to be significantly up-regulated. Recently, a number of studies have shown that CypB is important in the replication of several viruses, including Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), hepatitis C virus (HCV) and human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV 16). However, the function of cellular CypB in ORFV replication has not yet been explored.
Methods
Suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) technique was applied to identify genes differentially expressed in the ORFV-infected MDBK cells at an early phase of infection. Cellular CypB was confirmed to be significantly up-regulated by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis and Western blotting. The role of CypB in ORFV infection was further determined using Cyclosporin A (CsA) and RNA interference (RNAi). Effect of CypB gene silencing on ORFV replication by 50% tissue culture infectious dose (TCID50) assay and qRT-PCR detection.
Results
In the present study, CypB was found to be significantly up-regulated in the ORFV-infected MDBK cells at an early phase of infection. Cyclosporin A (CsA) exhibited suppressive effects on ORFV replication through the inhibition of CypB. Silencing of CypB gene inhibited the replication of ORFV in MDBK cells. In conclusion, these data suggest that CypB is critical for the efficient replication of the ORFV genome.
Conclusions
Cellular CypB was confirmed to be significantly up-regulated in the ORFV-infected MDBK cells at an early phase of infection, which could effectively facilitate the replication of ORFV.
Keywords: ORFV, Cellular cyclophilin B, Cyclosporine A, RNA interference, Replication
Background
Orf virus (ORFV) is the type species of the genus Parapoxvirus, which has a worldwide distribution and is the causative agent of Orf, a contagious debilitating skin disease of sheep and goats also known as contagious ecthyma, contagious pustular dermatitis, infectious labial dermatitis, scabby mouth or sore mouth [1]. Primary infections are usually resolved within 1–2 months, however repeated and persistent infections can occur in the presence of an intensive inflammatory host antivirus immune response [2, 3]. The mechanisms that establish the repeated and persistent infections in vivo are almost completely unknown. Currently, the host immune response to ORFV has been extensively studied, yet many aspects of the complex host-virus interactions remain unclear.
Cyclophilins (Cyp) comprise a family of peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerases, which are originally discovered as a cellular factor with high affinity for the immunosuppressant CsA [4, 5]. CypB is one of the most abundant members among the Cyp family, is ubiquitously expressed in most cells, and predominantly resides in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) through the ER retention signal sequence in the C-terminus [6, 7]. CypB functions in various cellular processes, including transcriptional regulation, protein secretion, immune response and apoptosis [8–10]. In addition, some researchers have shown that many viruses such as Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), hepatitis C virus (HCV) and human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV 16) require CypB for their replication [11–13]. However, there has been no report on the involvement of CypB in the replication of ORFV.
In the present study, CypB was found to be significantly up-regulated in the ORFV-infected MDBK cells at an early phase of infection. However, the function of cellular CypB in ORFV replication has not yet been explored. Sequently, we investigated the role of CypB in the replication of ORFV in MDBK cells. Cyclosporin A (CsA) exhibited suppressive effects on ORFV replication through the inhibition of CypB. Silencing of CypB gene inhibited the replication of ORFV in MDBK cells. In conclusion, these data suggest that CypB is critical for the efficient replication of the ORFV genome.
Methods
Cells and virus
The Madin―Darby bovine kidney (MDBK) cells were maintained in minimal essential medium (MEM) (GIBCO, Invitrogen), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and penicillin (100 U/mL); streptomycin (100 mg/mL); and nystatin (20 mg/mL). The Orf virus used in this study (ORFV-Jilin) was isolated using MDBK cells from scab specimens collected from skin lesions of a 6-week-old small-tailed Han sheep afflicted with orf in November 2008 in the Jilin province of China [14].
Antibodies and reagents
The antibodies used in this study were anti-Cyclophilin B polyconal rabbit antibody (Abcam), PE-Cy5 conjugated rabbit anti-Cyclophilin B antibody (Bioss), anti-β-actin (Proteintech), Peroxidase-conjugated Affinipure Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (Proteintech) and Peroxidase-conjugated Affinipure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (Proteintech). CsA were purchased from Sigma. PolyATtract® mRNA Isolation Systems was purchased from Promega. PCR-Select™ cDNA Subtraction Kit and Advantage cDNA PCR Kit & Polymerase Mix were obtained from Clontech. X-treme GENE HP DNA Transfection Reagent and X-treme GENE siRNA Transfection Reagent were purchased from Roche.
Virus infection
MDBK cells have been reported to be least partially permissive for ORFV replication [14]. A confluent monolayer of MDBK cells cultured in 75-cm2 flasks were adsorbed with ORFV-Jilin (multiplicity of infection [MOI] = 3) for 2 h at 37 °C. After adsorption, unbound virus was removed by gentle washing with serum-free medium followed by the addition of fresh medium and further incubation at 37 °C. At 2 h after further incubation, ORFV transcripts were detected in MDBK cells infected with ORFV-Jilin. Thus, the starting point of early phase of ORFV infection was determined for 4 h. The cultures of incubated cells were harvested at 4 h post infection, and cell lysates were collected. Normal cell controls were collected in a similar manner. All samples were frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C until SSH library construction.
Construction and screening of Suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) library
Total RNA was isolated from both mock- and ORFV-inoculated cell lysates using RNAiso Plus (Takara, Dalian, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The quality of total RNA were determined by ultraviolet spectrophotometry (260 and 280 nm) and 1% agarose/ethidium bromide (EtBr) gel electrophoresis. Messenger RNA (mRNA) was isolated from total RNA using PolyATtract® mRNA Isolation Systems (Promega) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The purified mRNA was treated with 1 mL of 75% ethanol and 0.1 volume of 3 mol/L NaOAc and used as the starting material to construct the SSH cDNA library. PCR select cDNA subtraction was conducted using PCR-Select™ cDNA Subtraction Kit (Clontech, USA) with 2 μg of mRNA for each sample as starting material according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Subtraction hybridization was conducted to perform subtraction in both forward and reverse directions. After two rounds of hybridization, PCR was conducted to selectively amplify cDNAs differentially expressed between ORFV-inoculated and normal MDBK cells. Each PCR amplification described below was conducted using a thermal cycler MyCycler (Bio-Rad) in a total volume of 25 μL with 1 μL template DNA, 0.5 U of 50 × Advantage cDNA polymerase (Clontech, USA), 200 μM of each dNTP, and forward and reverse primers (1 μM each). The cDNA fragments for subtracted secondary PCR products were inserted into the pMD18-T vector (TaKaRa, Dalian, China) with T4 DNA ligase and transformed into DH5a Escherichia coli cells. The clones with recombinant plasmid were identified by the LB-ampicillin/IPTG/X-Gal medium colony screening. Recombinant white clones were selected randomly and amplified by PCR using the M13 primer to construct the corresponding SSH cDNA library. The clones that yielded a single PCR product were selected for the next analysis.
qRT-PCR analysis of CypB expression in ORFV-infected MDBK cells
Among the differentially expressed genes obtained by SSH technique, CypB was found to be significantly up-regulated in the ORFV-infected MDBK cells at an early phase of infection. The qRT-PCR method based on the CypB gene was applied to determine the mRNA expression level of CypB in MDBK cells infected with ORFV-Jilin (MOI = 3) for 0 h, 2 h, 4 h, 8 h, 12 h, 18 h and 24 h. The primer sets used in the study were specific for CypB (forward primer 5′-GAGACGGCACTGGAGGTAAG-3′; reverse primer 5′-TCGTGATGAAGAACTGGGAG-3′). Briefly, total RNA was isolated from both mock- and ORFV-inoculated cell lysates using RNAiso Plus (Takara, Dalian, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Then, 200 ng of each RNA sample was used in a Oligo (dT) cDNA synthesis. The qPCRs for CypB gene were performed in 20 μL of reaction mixture containing 10 μL SYBR Premix ExTaq (Takara, Dalian, China), 0.2 μM of each oligonucleotide primer, 100 ng of each cDNA sample, and 7.2 μL ddH2O. Each sample was repeated three times. Fluorescent signals were analyzed by an ABI PRISM 7000 (Applied Biosystems, Tokyo, Japan). Data were statistically analyzed by Student’s t-test using GraphPad Prism 6 software.
Western blotting analysis of CypB expression in ORFV-infected MDBK cells
The MDBK cells at hours 0, 2, 4, 8, 12, 18 and 24 post infection were washed thoroughly and lysed in cell lysis buffer (20 mM Tris [pH 7.5], 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, sodium pyrophosphate, β-glycerophosphate, EDTA, Na3VO4, leupeptin). The lysates were briefly sonicated and cleared by centrifugation for 5 min at 12,000 g at 4 °C. The lysates were further denatured by incubation for 10 min at 95 °C in sample buffer (2% SDS, 10% glycerol, 50 mM Tris [pH 6.8], 5% β-mercaptoethanol, 0.01% bromophenol blue). The samples were then subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes (Millipore, Bedford, MA). After incubation in blocking buffer (5% nonfat milk powder in PBS) for 1 h at room temperature, the membrane was reacted with anti-Cyclophilin B antibody (1:1000) overnight at 4 °C and HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:3000) for 1 h at 37 °C. The antibody-antigen complex was visualized by enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Anti-ORFV activity of CsA in vitro detected by MTT assay
MTT assay used for measuring cell survival and proliferation was performed in order to determine the effect of CsA on the inhibitory ratio of ORFV. Briefly, a confluent monolayer of MDBK cells grown on 96-well plates were inocubated with ORFV-Jilin (MOI = 0.1) and incubated in a CO2 incubator with a 5% CO2 atmosphere. After 2 h of adsorption, the maintenance medium containing various concentrations of CsA (0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 1.6, 3.2 μg/mL) was added after removing the virus inoculum. At 24 h after drug action, 100 μL MTT (tetrazolium salt 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) were added to each well and kept in a dark environment for 4 h at 37 °C. Then, MTT was aspirated and 100 μL well−1 of DMSO (Merck, Darmstad, Germany) was added to each well. Subsequently, the absorbance value at a wavelength of 570 nm was measured using a UV–visible spectrophotometer (LPB Pharmacia, Bromma, Sweden) for the calculating the inhibitory rate of CsA on ORFV proliferation. The untreated cell cultures were cultured under the same conditions. Data were statistically analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD) test using GraphPad Prism 6 software.
CypB gene silencing by siRNA
Based on the sequences of CypB, two pairs of siRNAs, CypB-specific siRNA and negative siRNA control (scrambled siRNA) were designed and synthesized by Shanghai GenePharma Co., Ltd. The sequences are shown in Table 1. The cells were grown on 12-well plates and incubated in a CO2 incubator with a 5% CO2 atmosphere. Approximately 50–60% confluent, the cells were transfected with 35 nM siRNA by using X-tremeGENE siRNA transfection reagent (Roche, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The transfected cells were then washed with MEM without serum and incubated in MEM supplemented with 2% fetal bovine serum. Untransfected MDBK cells were used as a control. Typical siRNA transfection efficiency was found to be 83% for MDBK cells as monitored by fluorescein-labeled control siRNA duplex. CypB knockdown was confirmed 48 h post siRNA transfection by qRT-PCR and Western blotting (data not shown).
Table 1.
List of siRNA sequences used in this study
| Name | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| CypB specific siRNA | up | GCAUCUACGGUGAACGCUUTT |
| down | AAGCGUUCACCGUAGAUGCTT | |
| Negative control siRNA | up | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT |
| down | ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT | |
Immunofluorescence assay after siRNA knockdown of CypB
The MDBK cells were mock-transfected or transfected with CypB siRNAs or scrambled siRNAs for 48 h and subjected to immunofluorescence assay. Cells cultured on glass slides were washed gently in phosphate buffered saline (PBS), and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min, PBS washed (three times, each 5 min); 0.2% Triton X-100 enhanced the permeability of cell membranes for 10 min at room temperature and PBS washed; 5% skim milk incubated 1 h, PBS washed. Then cells were incubated with PE-Cy5 conjugated rabbit anti-Cyclophilin B antibody (1:500) at 4 °C over the night. Cell nuclei were stained blue with DAPI for 15 min. Finally, the samples were washed three times with PBS and observed under immunofluorescent microscope.
Effect of CypB gene silencing on ORFV replication
At 48 h post siRNA transfection, the siRNA-treated cells were infected with ORFV-Jilin (MOI = 3), respectively. Viral DNA was extracted from cell cultures at 12 h, 24 h, 36 h, 48 h, 60 h and 72 h postinfection. The qPCR method based on the DNA polymerase gene of ORFV was applied to determine the viral DNA copy number. The qPCR assay was performed as described previously [15]. Furthermore, viral yields were quantitated in the siRNA-treated cells by the 50% tissue culture infectious dose (TCID50) method. Briefly, the siRNA-treated cells were infected with 100 TCID50 (106.5) of ORFV, and the infection was allowed to proceed for the indicated time periods. Untransfected MDBK cells were used as a control. Data were statistically analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD test using GraphPad Prism 6 software.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out using GraphPad Prism v6.0 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA). Student’s t-test and one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD test were used for comparisons of two and multiple groups, respectively. Data were expressed as the means with error bars depicting ± SEM, and differences were considered statistically significant at * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001.
Results
CypB was found to be significantly up-regulated in the ORFV-infected MDBK cells by SSH technique
In order to explore host genes inovolved in the process of ORFV invasion, the differentially expressed genes from ORFV-infected MDBK cells at an early phase of infection were identified using SSH technique. A total of 81 expressed sequence tags (ESTs) were obtained from the SSH libraries by sequencing and alignment. Among of all the ESTs, 60 ESTs came from the forward SSH library and 21 ESTs came from the reverse SSH library. BLAST analysis against the Genbank database revealed that 79 ESTs showed significantly homology to known genes. Of those, all the ESTs showed significantly homology with Bos Taurus related sequences (Tables 2 and 3). CypB as an important member of cyclophilins family, was found to be significantly up-regulated in the ORFV-infected MDBK cells at an early phase of infection.
Table 2.
Similarity between expressed sequence tags in the forward suppression subtractive hybridization library and genes in GenBank
| EST No. | Species | Gene homology | Gene name | Fold upregulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-1 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus beta-actin (ACTB) mRNA | ACTB | 1.5 |
| F-2 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus actin, gamma 1 (ACTG1), mRNA | ACTG1 | 1.7 |
| F-3 | unknown | unknown | unknown | 3.4 |
| F-4 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus vacuole membrane protein 1 (VMP1), mRNA | VMP1 | 3.7 |
| F-5 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus ring finger protein 19B (RNF19B), mRNA | RNF19B | 1.9 |
| F-6 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus zinc finger protein 408 (ZNF408), mRNA | ZNF408 | 2.3 |
| F-7 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus zinc finger CCCH-type containing 14 (ZC3H14), transcript variant 1, mRNA | ZC3H14 | 1.5 |
| F-8 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus ATPase, Na+/K+ transporting, beta 1 polypeptide (ATP1B1), mRNA. | ATP1B1 | 3.4 |
| F-9 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus poly-U binding splicing factor 60KDa (PUF60), mRNA. | PUF60 | 2.3 |
| F-10 | unknown | unknown | unknown | 2.6 |
| F-11 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3, subunit L (EIF3L), mRNA | EIF3L | 3.7 |
| F-12 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 alpha 1 EEF1A1), mRNA | EEF1A1 | 3.4 |
| F-13 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5 (EIF5), mRNA | EIF5 | 2.9 |
| F-14 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus cytohesin 2 (CYTH2), mRNA | CYTH2 | 1.6 |
| F-15 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus transmembrane emp24 protein transport domain containing 1 (TMED1), mRNA | TMED1 | 3.6 |
| F-16 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus transmembrane protein 179B (TMEM179B), mRNA | TMEM179B | 2.8 |
| F-17 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus neuropilin 2 (NRP2), mRNA | NRP2 | 2.1 |
| F-18 | Bos Taurus | Sin3A-associated protein, 18 kDa (SAP18), mRNA | SAP18 | 2.4 |
| F-19 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus renin binding protein (RENBP), mRNA | RENBP | 1.3 |
| F-20 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus signal sequence receptor, alpha (SSR1), mRNA | SSR1 | 1.9 |
| F-21 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 (MAP2K6), mRNA | MAP2K6/MKK6 | 9.2 |
| F-22 | Bos Taurus | Bos Taurus solute carrier family 1 (neuronal/epithelial high affinity glutamate transporter, system Xag), member 1 (SLC1A1), mRNA. | SLC1A1 | 2.7 |
| F-23 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus isolate Mcg489 mitochondrion, complete genome | Mcg489 mitochondrion | 2.5 |
| F-24 | Bos Taurus | Calmodulin 1 (phosphorylase kinase, delta) (CALM1), mRNA | CALM1 | 2.3 |
| F-25 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus enhancer of rudimentary homolog (Drosophila) (ERH), mRNA | ERH | 1.7 |
| F-26 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus threonyl-tRNA synthetase-like 1 (TARSL1), mRNA, complete cds. | TARSL1 | 2.1 |
| F-27 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus threonyl-tRNA synthetase 2, mitochondrial (putative) (TARS2), mRNA | TARS2 | 1.8 |
| F-28 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus S100 calcium binding protein A2 (S100A2), mRNA | S100A2 | 9.7 |
| F-29 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus lactate dehydrogenase B (LDHB), mRNA, complete cds. | LDHB | 3.5 |
| F-30 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus H3 histone, family 3A (H3F3A), mRNA. | H3F3A | 4.2 |
| F-31 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U (scaffold attachment factor A) (HNRNPU), mRNA. | HNRNPU | 2.9 |
| F-32 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus RAB2A, member RAS oncogene family (RAB2A), mRNA. | RAB2A | 1.5 |
| F-33 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus alanyl-tRNA synthetase (AARS), mRNA | AARS | 1.9 |
| F-34 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus minichromosome maintenance complex component 4 (MCM4), mRNA | MCM4 | 2.7 |
| F-35 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus tubulin, beta 6, mRNA | TUBB6 | 1.3 |
| F-36 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus tubulin, alpha 1c (TUBA1C), mRNA | TUBA1C | 1.7 |
| F-37 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus tubulin, alpha 1b (TUBA1B), mRNA | TUBA1B | 1.2 |
| F-38 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus tropomyosin 1 (alpha) (TPM1), mRNA | TPM1 | 2.0 |
| F-39 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus tropomyosin 4 (TPM4), mRNA | TPM4 | 1.5 |
| F-40 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus minichromosome maintenance complex component 6 (MCM6), mRNA | MCM6 | 2.3 |
| F-41 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus chromosome 10 open reading frame, human C14orf1 (C10H14orf1), mRNA. | C10H14orf1 | 2.4 |
| F-42 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus CLPTM1-like (CLPTM1L), mRNA | CLPTM1L | 4.3 |
| F-43 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus CD151 molecule (Raph blood group) (CD151), mRNA | CD151 | 7.6 |
| F-44 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase binding protein (UQCRB), mRNA. | UQCRB | 2.6 |
| F-45 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus low molecular mass ubiquinone-binding protein mRNA, complete cds. | Low molecular mass ubiquinone-binding protein | 2.1 |
| F-46 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus dynein, cytoplasmic 1, light intermediate chain 1 (DYNC1LI1), mRNA | DYNC1LI1 | 3.5 |
| F-47 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (GPI), mRNA | GPI | 2.9 |
| F-48 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus galactosidase, beta 1 (GLB1), mRNA | GLB1 | 2.4 |
| F-49 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus proteasome (prosome, macropain) activator subunit 1 (PA28 alpha) (PSME1), mRNA. | PSME1 | 1.3 |
| F-50 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus peptidylprolyl isomerase B (cyclophilin B) (PPIB), mRNA | PPIB | 10.2 |
| F-51 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus peroxiredoxin 2 (PRDX2), mRNA. | PRDX2 | 3.4 |
| F-52 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus proteolipid protein 2 (colonic epithelium-enriched) (PLP2), mRNA. | PLP2 | 3.7 |
| F-53 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus voucher proven bull 27,223 mitochondrion, complete genome. | Bos taurus voucher proven bull 27,223 mitochondrion | 2.1 |
| F-54 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus Fas-activated serine/threonine kinase (FASTK), mRNA. | FASTK | 4.6 |
| F-55 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus ferritin, light polypeptide (FTL), mRNA | FTL | 2.5 |
| F-56 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus Finkel-Biskis-Reilly murine sarcoma virus (FBR-MuSV) ubiquitously expressed (FAU), mRNA. | FAU | 1.2 |
| F-57 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus acyl-CoA thioesterase 7 (ACOT7), mRNA | ACOT7 | 1.9 |
| F-58 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT), mRNA | APRT | 1.5 |
| F-59 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus mannosyl (alpha-1,3-)-glycoprotein beta-1,2-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (MGAT1), mRNA, complete cds | MGAT1 | 1.7 |
| F-60 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus lactate dehydrogenase C (LDHC), transcript variant 1, mRNA. | LDHC | 2.3 |
Table 3.
Similarity between expressed sequence tags in the rverse suppression subtractive hybridization library and genes in GenBank
| EST No. | Species | Gene homology | Gene name | Fold downregulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-1 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 (MAP2K4), mRNA. | MAP2K4/MKK4 | 8.7 |
| R-2 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus neuroplastin (NPTN), mRNA | NPTN | 1.9 |
| R-3 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus nuclear transport factor 2 (NUTF2), mRNA | NUTF2 | 2.5 |
| R-4 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus S100 calcium binding protein A4 (S100A4), mRNA | S100A4 | 9.6 |
| R-5 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 5 (ACSL5), mRNA, complete cds | ACSL5 | 2.9 |
| R-6 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus eukaryotic translation elongation factor 2 (EEF2), mRNA | EEF2 | 3.8 |
| R-7 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus poly-U binding splicing factor 60KDa (PUF60), mRNA | PUF60 | 1.3 |
| R-8 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus H3 histone, family 3B (H3.3B) (H3F3B), mRNA | H3F3B | 2.6 |
| R-9 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), mRNA | GAPDH | 1.2 |
| R-10 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) complex I, assembly factor 1 (NDUFAF1), mRNA | NDUFAF1 | 1.7 |
| R-11 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus solute carrier family 51, beta subunit (SLC51B), mRNA | SLC51B | 3.2 |
| R-12 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus ferredoxin 1 (FDX1), mRNA | FDX1 | 2.5 |
| R-13 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus transforming growth factor beta 1 induced transcript 1 (TGFB1I1), mRNA | TGFB1I1 | 1.4 |
| R-14 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus heat shock 70 kDa protein 8 (HSPA8), mRNA | HSPA8 | 10.2 |
| R-15 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus vimentin (VIM), mRNA | VIM | 6.4 |
| R-16 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus lectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 1 (LGALS1), mRNA | LGALS1 | 2.1 |
| R-17 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus clone IMAGE:7,961,517 NDP kinase NBR-A mRNA, complete cds | NDP kinase NBR-A | 1.5 |
| R-18 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus polymerase (RNA) I polypeptide D (POLR1D), mRNA | POLR1D | 1.5 |
| R-19 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha inhibiting activity polypeptide 1 (GNAI1), mRNA | GNAI1 | 1.2 |
| R-20 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus annexin A2 (ANXA2), mRNA | ANXA2 | 1.9 |
| R-21 | Bos Taurus | Bos taurus Williams Beuren syndrome chromosome region 22 (WBSCR22), mRNA | WBSCR22 | 2.3 |
Verification of the mRNA expression levels of CypB gene by qRT-PCR
We further verified the mRNA expression levels of CypB gene by qRT-PCR (Fig. 1a). CypB was confirmed by qRT-PCR as differentially expressed. The transcript levels of CypB was overexpressed in MDBK cells infected with ORFV-Jilin compared with mock-infected MDBK cells (Fig. 1b), with CypB mRNA levels 106-fold higher in ORFV-infected MDBK cells at 4 h post infection than in the corresponding mock-infected MDBK cells.
Fig. 1.
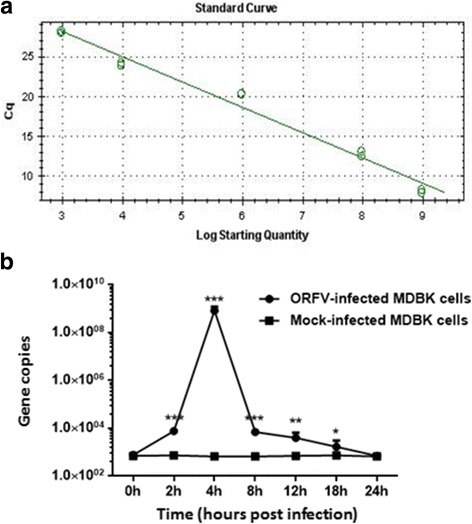
Verification of the mRNA expression levels of CypB gene identified from the forward SSH library by qRT-PCR. a According to qRT-PCR, the standard curve established showed an efficiency of 106.7% with R2 of 0.991. b The mRNA expression levels of CypB gene in mock- and ORFV-infected MDBK cells at 0, 2, 4, 8, 12, 18 and 24 h post infection were measured by qRT-PCR. Statistical analysis was performed by Student’s t-test using GraphPad Prism 6 software. Values are the means ± SEM. (* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001). As shown in Fig. 1b, the transcript levels of CypB was overexpressed in MDBK cells infected with ORFV-Jilin (MOI = 3) compared with mock-infected MDBK cells, with CypB mRNA levels 106-fold higher in ORFV-infected MDBK cells at 4 h post infection than in the corresponding mock-infected MDBK cells
Verification of the protein expression levels of CypB by Western blotting
The expression of CypB gene was confirmed by Western blotting using β-actin as an internal control. Western blot analysis showed increased expression in the ORFV-infected MDBK cells, especially at 4 h post infection (Fig. 2). The results were consistent with those obtained from qRT-PCR. These findings suggested that changes in the expression of CypB gene and protein are associated with ORFV early infection.
Fig. 2.
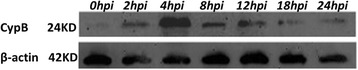
Verification of the protein expression levels of CypB gene identified from the forward SSH library with western blotting. The MDBK cells at hours 0, 2, 4, 8, 12, 18 and 24 post infection were collected and lysed in cell lysis buffer (20 mM Tris [pH 7.5], 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, sodium pyrophosphate, β-glycerophosphate, EDTA, Na3VO4, leupeptin). The lysates were subjected to SDS/PAGE and Western blot analysis with anti-Cyclophilin B antibody (diluted with 1:1000). β-actin was used as an internal control. An increased expression of CypB gene was observed in the ORFV-infected MDBK cells, especially at 4 h post infection. There were no obvious changes observed in the levels of β-actin
Inhibition effect of CsA on ORFV proliferation in MDBK cells
The inhibition of CsA on ORFV proliferation in vitro was evaluated by MTT assay. The MDBK cells infected with ORFV were exposed to increasing concentrations of CsA from 0 to 3.2 μg/mL and maximal ethanol concentration used to solubilize and dilute CsA as vehicle. As demonstrated in Fig. 3, the inhibition rate was increased in different concentrations of CsA (0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 1.6, 3.2 μg/mL) in comparision with the control (no treatment) and this increase was significant in 0.2 μg/mL (*** P < 0.001). Our results showed that treatment with 0.2 μg/mL CsA could effectively inhibit the cytotoxicity induced by ORFV.
Fig. 3.
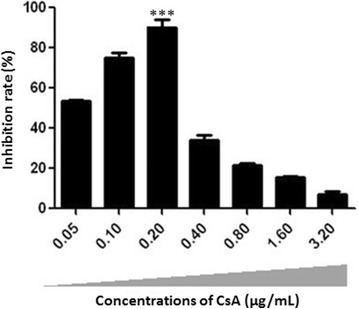
Inhibition effect of CsA on ORFV proliferation in MDBK cells. The MDBK cells infected with ORFV (MOI = 0.1) were exposed to increasing concentrations of CsA (0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 1.6, 3.2 μg/mL) and maximal ethanol concentration used to solubilize and dilute CsA as vehicle. The anti-ORFV activity of CsA in vitro was detected by MTT assay. Subsequently, the absorbance value at a wavelength of 570 nm was measured for the calculating the inhibitory rate of CsA on ORFV proliferation. The untreated cells were cultured under the same conditions. Data were statistically analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD test using GraphPad Prism 6 software. Values are the means ± SEM. (*** P < 0.001). The results showed that treatment with 0.2 μg/mL CsA could effectively inhibit the cytotoxicity induced by ORFV
Examination of siRNA effect by Immunofluorescence assay
The immunofluorescence assay was performed in order to determine the inhibitory effect of CypB specific siRNAs. As shown in Fig. 4, the CypB-specific red fluorescence signals distributed in the cytoplasm of MDBK cells was found to be attenuated at 48 h post transfection. The cells transfected with scrambled siRNAs exhibited relative apparent fluorescent signals, which was similar to that in mock-transfected cells. However, no red fluorescence signals were observed in the cells transfected with CypB specific siRNAs. Nuclei were stained blue with DAPI.
Fig. 4.
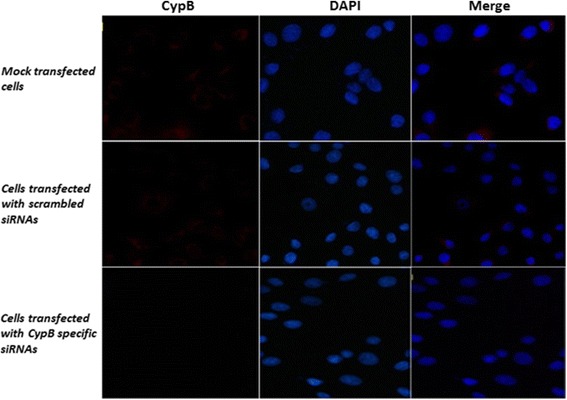
Examination of siRNA effect by Immunofluorescence assay. The MDBK cells were mock-transfected or transfected with CypB siRNAs or scrambled siRNAs for 48 h and subjected to immunofluorescence assay. As shown in Fig. 4, the CypB-specific red fluorescence signals distributed in the cytoplasm of MDBK cells were found in the cells transfected with scrambled siRNAs, which was similar to that in mock-transfected cells. However, no red fluorescence signals were observed in the cells transfected with CypB specific siRNAs. Nuclei were stained blue with DAPI
Examination of siRNA effect by qPCR
To quantify the effect of siRNA on viral replication, the viral genome copy number was determined at 12 h, 24 h, 36 h, 48 h, 60 h and 72 h postinfection by qPCR based on the DNA polymerase gene of ORFV. The results indicated a marked reduction in the relative expression level of viral genome copies, compared to the mock group at 12 h, 24 h, 36 h, 48 h, 60 h and 72 h postinfection, when the CypB specific siRNA were used. At 48 h postinfection, the number of viral genome copies of the siRNA-treated cells was only 1 % in the ORFV-infected cells (Fig. 5a).
Fig. 5.
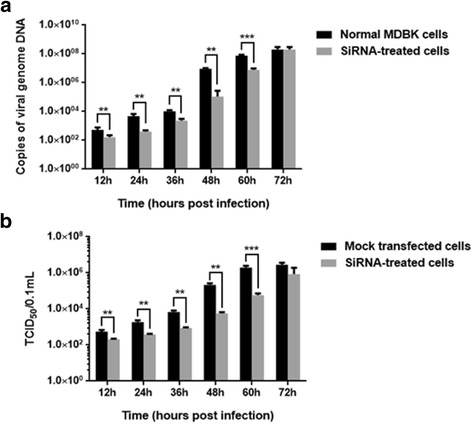
The inhibitory effect of of CypB specific siRNAs on ORFV replication in MDBK cells. a At 48 h post siRNA transfection, the siRNA-treated cells were infected with ORFV-Jilin, respectively. Viral DNA was extracted from cell cultures at 12, 24, 36, 48, 60 and 72 h postinfection. The qPCR method based on the DNA polymerase gene of ORFV was applied to determine the viral DNA copy number. b Viral yields were quantitated in the siRNA-treated cells by TCID50 assay. TCID50 values are the means of three repeat titrations at the same points indicated. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD test. Values are the means ± SEM. (** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001)
Examination of siRNA effect by infectious virus assay
To further investigate the inhibitory effect of siRNAs, the microtiter method was used for titration of ORFV at 5 days postinfection. The results (Fig. 5b) showed that viral titers in untransfected MDBK cells was higher than in the siRNA-treated cells at 12 h, 24 h, 36 h, 48 h, 60 h and 72 h postinfection. In untransfected MDBK cells, titers reached a peak of around 1 × 106.3/0.1 mL (TCID50) at 60 h postinfection, however, titers reached similar values in the siRNA-treated cells at 72 h postinfection.
Discussion
Viruses are strict intracellular pathogens that require the cellular environment to complete a successful infection. During the infection process, viruses could affect several major cellular responses by altering the expression of the key host genes. Considering viral infection strongly relies on several factors from the host, the study of virus-host interactions is essential to the understanding of the infection process of disease and the mechanism of the virus persistence in the host, and to help with the development of effective vaccines and perhaps the cure of viral infections.
ORFV is a highly epitheliotropic virus, that infects damaged or scarified skin and replicates in regenerating epidermal keratinocytes. An important characteristic of the virus is its ability to cause repeated and persistent infections [16] even in the presence of an intensive inflammatory and multiple host immune response [3, 17]. At present, little is known about the mechanisms of ORFV infection of host, although several studies have demonstrated that ORFV encoded protein might interact with a host protein involved in the pathway and/or might mimic the structurally similar host protein to invade/manipulate the cellular pathway [18, 19].
With the purpose of identify genes involved in ORFV early invasion, we constructed a cDNA library and identified the differently expressed genes from ORFV-infected MDBK cells at an early phase of infection in the study. By using SSH technique, a total of 81 EST sequences with differing functions were identified, including 60 differently up-regulated genes from the forward library and 21 differently down-regulated genes from the reverse library. CypB as an important member of cyclophilins family, was found to be significantly up-regulated in the ORFV-infected MDBK cells at an early phase of infection. In the present study, the upregulation of CypB in host cells was further validated by qRT-PCR and Western blotting. The results showed that CypB was overexpressed in MDBK cells infected with ORFV-Jilin at 4 h post infection, which were consistent with those obtained by SSH technique.
Recently, increasing studies have demonstrated that cellular CypB are closely related with viral infections such as JEV [11], HCV [12] and HPV 16 [13]. However, the role of CypB in ORFV proliferation have remained unknown. By using CsA, we determined that it could effectively inhibit the cytotoxicity induced by ORFV, which suggested that CypB was required for the efficient proliferation of ORFV in vitro. To further ascertain the regulatory role of CypB for ORFV replication, CypB specific siRNAs were synthesized and then transfected. The efficiency of inhibition of viral replication was evaluated by immunofluorescence assay, qPCR and infectious virus assay. The results demonstrated that silencing of CypB gene by RNAi could efficiently inhibit ORFV genome replication and infectious virus production. On the basis of the above studies, CypB has been confirmed to facilitate ORFV replication.
Moreover, CypB has been demonstrated to involve in inflammatory events [20]. The overexpressed CypB could activate the extracellular signal-regulated kinase intracellular signaling pathway such as ERK signaling through binding with CD147, which has been shown to function as a signalling receptor for CypB to mediate chemotactic activity towards a variety of immune cells [21–23]. Currently, the upregulation of CypB has been confirmed to facilitate ORFV replication, presumably through interactions with CD147 or other some agents to activate the associated immunological and inflammatory signaling pathways. Further investigations on the cooperation between these molecules might provide new insights on the mechanisms controlling ORFV infection within target cells and lead to the development of new therapeutic tools to block the virus infection.
Conclusions
The results of the present study demonstrated that CypB could effectively facilitate the replication of ORFV, suggesting CypB might be involved in the process of ORFV infection. However, the detailed interaction between CypB and ORFV is still unknown. Further studies will be focused on the interplay between ORFV and cellular CypB, which may contribute to clarify virus pathogenesis and the development of antiviral vaccine candidates and novel inhibitors.
Acknowledgements
Financial support for this study was obtained from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 31672554), the Key scientific and technological project of Jilin Province (Grant number 20140204076NY), the Funding of world bank financed project of Jilin Province (Grant number 2011-Y20), and the program Supported by Jilin University for the Excellent Youth Scholars (Grant number 419080500593).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (31672554), Key scientific and technological project of Jilin Province (20140204076NY), Funding of world bank financed project of Jilin Province (2011-Y20) and the program Supported by Jilin University for the Excellent Youth Scholars (419080500593).
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during the study are included in this study.
Authors’ contributions
KZ and FG conceived the study and participated in its design and coordination. JL, XZ, YZ and DZ performed the experiments. KZ, WH and DS analyzed the data and wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations
- CsA
Cyclosporin A
- CypB
Cyclophilin B
- ESTs
Expressed sequence tags
- EtBr
Ethidium bromide
- FBS
Fetal bovine serum
- HCV
Hepatitis C virus
- HPV 16
Human papillomavirus type 16
- JEV
Japanese encephalitis virus
- MDBK
Madin―Darby bovine kidney cells
- MEM
Minimal essential medium
- MOI
Multiplicity of infection
- mRNA
Messenger RNA
- MTT
Tetrazolium salt 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- ORFV
Orf virus
- PBS
Phosphate buffered saline.
- PPIase
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase
- RNAi
RNA interference
- SDS-PAGE
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- TCID50
50% tissue culture infectious dose
Contributor Information
Kui Zhao, Email: kuizhao@jlu.edu.cn.
Jida Li, Email: 282470735@qq.com.
Wenqi He, Email: hewq@jlu.edu.cn.
Deguang Song, Email: songdg6301@126.com.
Ximu Zhang, Email: ximuzhang@pku.edu.cn.
Di Zhang, Email: 1286226494@qq.com.
Yanlong Zhou, Email: 619327871@qq.com.
Feng Gao, Email: gaofeng@jlu.edu.cn.
References
- 1.Chan KW, Lin JW, Lee SH, Liao CJ, Tsai MC, Hsu WL, Wong ML, Shih HC. Identification and phylogenetic analysis of orf virus from goats in Taiwan. Virus Genes. 2007;35(3):705–712. doi: 10.1007/s11262-007-0144-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hosamani M, Scagliarini A, Bhanuprakash V, McInnes CJ, Singh RK. Orf: an update on current research and future perspectives. Expert Rev Antiinfect Ther. 2009;7:879–893. doi: 10.1586/eri.09.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Haig DM, McInnes CJ. Immunity and counter-immunity during infection with the parapoxvirus orf virus. Virus Res. 2002;88:3–16. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1702(02)00117-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Handschumacher RE, Harding MW, Rice J, Drugge RJ, Speicher DW. Cyclophilin: a specific cytosolic binding protein for cyclosporin A. Science. 1984;226:544–547. doi: 10.1126/science.6238408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schreiber SL. Chemistry and biology of the immunophilins and their immunosuppressive ligands. Science. 1991;251:283–287. doi: 10.1126/science.1702904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Price ER, Jin M, Lim D, Pati S, Walsh CT, Mckeon FD. Cyclophilin B trafficking through the secretory pathway is altered by binding of cyclosporin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91(9):3931–3935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wang P, Heitman J. The cyclophilins. Genome Biol. 2005;6(7):226. doi: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-7-226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rycyzyn MA, Clevenger CV. The intranuclear prolactin/cyclophilin B complex as a transcriptional inducer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(10):6790–6795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.092160699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Allain F, Denys A, Spik G. Cyclophilin B mediates cyclosporin A incorporation in human blood T-lymphocytes through the specific binding of complexed drug to the cell surface. Biochem J. 1996;317(Pt 2):565–570. doi: 10.1042/bj3170565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kim J, Choi TG, Ding Y, Kim Y, Ha KS, Lee KH, Kang I, Ha J, Kaufman RJ, Lee J, Choe W, Kim SS. Overexpressed cyclophilin B suppresses apoptosis associated with ROS and Ca2+ homeostasis after ER stress. J Cell Sci. 2008;121(Pt 21):3636–3648. doi: 10.1242/jcs.028654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kambara H, Tani H, Mori Y, Abe T, Katoh H, Fukubara T, Taguwa S, Moriishi K, Matsuura Y. Involvement of cyclophilin B in the replication of Japanese encephalitis virus. Virology. 2011;412:211–219. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Watashi K, Ishii N, Hijikata M, Inoue D, Murata T, Miyanari Y, Shimotohno T. Cyclophilin B is a functional regulator of Hepatitis C virus RNA polymerase. Mol Cell. 2005;19:111–122. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bienkowska-Haba M, Patel HD, Sapp M. Target cell cyclophilins facilitate human papillomavirus type 16 infection. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5(7) doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhao K, Song D, He W, Lu H, Zhang B, Li C, Chen K, Gao F. Identification and phylogenetic analysis of an Orf virus isolated from an outbreak in sheep in the Jilin province of China. Vet Microbiol. 2010;142:408–415. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2009.10.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Li J, Song D, He W, Bao Y, Lu R, Su G, Wang G, Lu H, Zhao K, Gao F. Rapid detection of orf virus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification based on the DNA polymerase gene. Arch Virol. 2013;158:793–798. doi: 10.1007/s00705-012-1526-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ndikuwera J, Odiawo GO, Usenik EA, Kock ND, Ogaa JS, Kuiper R. Chronic contagious ecthyma and caseous lymphadenitis in two Boer goats. Vet Rec. 1992;131(25–26):584–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Diel DG, Delhon G, Luo S, Flores EF, Rock DL. A novel inhibitor of the NF-{kappa}B signaling pathway encoded by the parapoxvirus orf virus. J Virol. 2010;84:3962–3973. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02291-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Deane DL, McInnes CJ, Percival A, Wood A, Thomson J, Lear A, Gilray J, Fleming S, Mercer A, Haig D. Orf virus encodes a novel secreted protein inhibitor of granulocyte-macrophage clony-stimulating factor and interleukin-2. J Virol. 2000;74:1313–1320. doi: 10.1128/JVI.74.3.1313-1320.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fleming SB, Haig DM, Nettleton P, Reid HW, McCaughan CA, Wise LM, Mercer AA. Sequence and functional analysis of a homolog of interleukin-10 encoded by the parapoxvirus orf virus. Virus Genes. 2000;21:85–95. doi: 10.1023/B:VIRU.0000018443.19040.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Arora K, Gwinn WM, Bower MA, Watson A, Okwumabua I, MacDonald HR, Bukrinsky MI, Constant SL. Extracellular cyclophilins contribute to the regulation of inflammatory responses. J Immunol. 2005;175(1):517–522. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.1.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kim K, Kim H, Jeong K, Jung MH, Hahn BS, Yoon KS, Jin BK, Jahng GH, Kang I, Ha J, Choe W. Release of overexpressed CypB activates ERK signaling through CD147 binding for hepatoma cell resistance to oxidative stress. Apoptosis. 2012;17(8):784–796. doi: 10.1007/s10495-012-0730-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yurchenko V, O'Connor M, Dai WW, Guo H, Toole B, Sherry B, Bukrinsky M. CD147 is a signaling receptor for cyclophilin B. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;288(4):786–788. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yurchenko V, Constant S, Eisenmesser E, Bukrinsky M. Cyclophilin-CD147 interactions: a new target for anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010;160(3):305–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04115.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during the study are included in this study.


