Fig. 1.
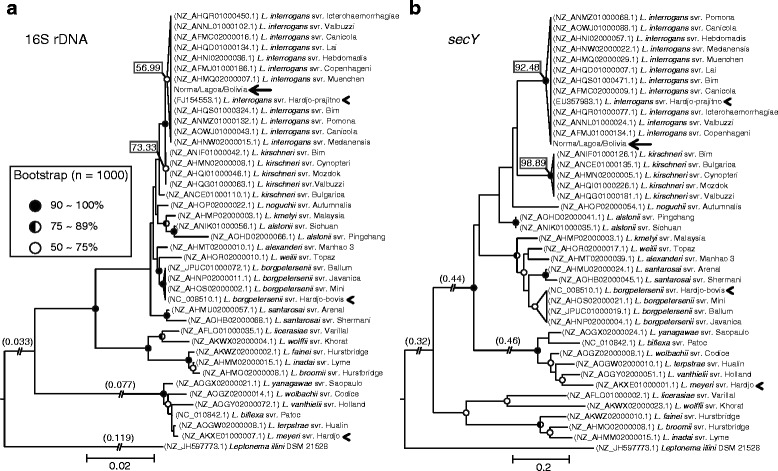
Phylogenetic trees of Leptospira spp. using (a) 16S rDNA and (b) secY sequences. The nucleotide sequences were aligned using Muscle, and the trees were generated using the neighbor-joining method (bootstrap: 1.000, model maximum composite likelihood). The clinical isolates from this work are indicated with arrows. Leptospira strains of the Hardjo serovar are indicated with arrowheads. Circles at nodes reflect the bootstrap support. An ancestral node without a circle indicates a bootstrap value below 50%. The bootstrap values of the nodes that group L. interrogans or L. kirschneri are located on these nodes in rectangles. Long branches are broken, and the real lengths are displayed on these branches in parenthesis. In both trees, orthologous sequences from Leptonema illini DSM 21528 were used as the outgroup
