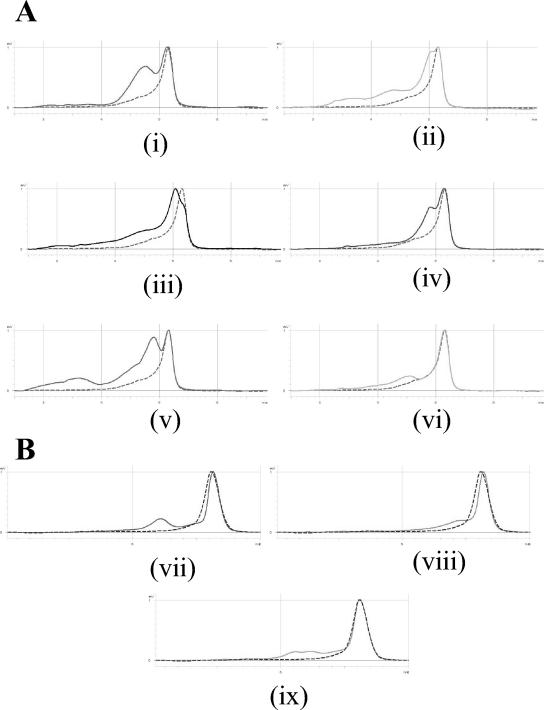
FIG. 1.
DHPLC elution traces for C. jejuni and C. coli isolates with mutations in gyrA. (A) C. jejuni (i) type A (Thr-86→Ile, ACA→ATA), (ii) type B (His-81, CAC→CAT; Thr-86→Ile, ACA→ATA), (iii) type C (His-81, CAC→CAT; Thr-86→Ile, ACA→ATA; Ser-119, AGT→AGC; Ala-120, GCC→GCT), (iv) type G (Asp-90→Asn, GAT→AAT), (v) type E (His-81, CAC→CAT; Thr-86→Ile, ACA→ATA; Gly-110, GGC→GGT), and (vi) type F (His-81, CAC→CAT; Thr-86→Ala, ACA→GCA). (B) C. coli (vii) CC/A (Thr-86→Ile, ACT→ATT; Phe-99, TTT→TTC), (viii) CC/B (His-81, CAC→CAT; Thr-86→Ile, ACA→ATA; Gly-113, GGA→GGT; Ile-115, ATA→ATC), and (ix) CC/C (Val-60→Ile, GTA→ATA; Phe-99, TTT→TTC). The wild-type pattern (dotted line) is shown on each elution trace: C. jejuni NCTC 11168 (A) and C. coli NCTC 11366 (B). Isolates with gyrA code CC/B were C. coli but had a gyrA sequence with a closer identity to that of C. jejuni (the nucleotide changes shown are differences from the C. jejuni gyrA sequence). The polymorphisms seen at His-81 (CAT), Gly-113 (GGT), Ile-115 (ATC), and Ala-120 (GCT) in C. jejuni are present in wild-type C. coli (40).