Figure 1. Mechanism of ecCTPS assembly.
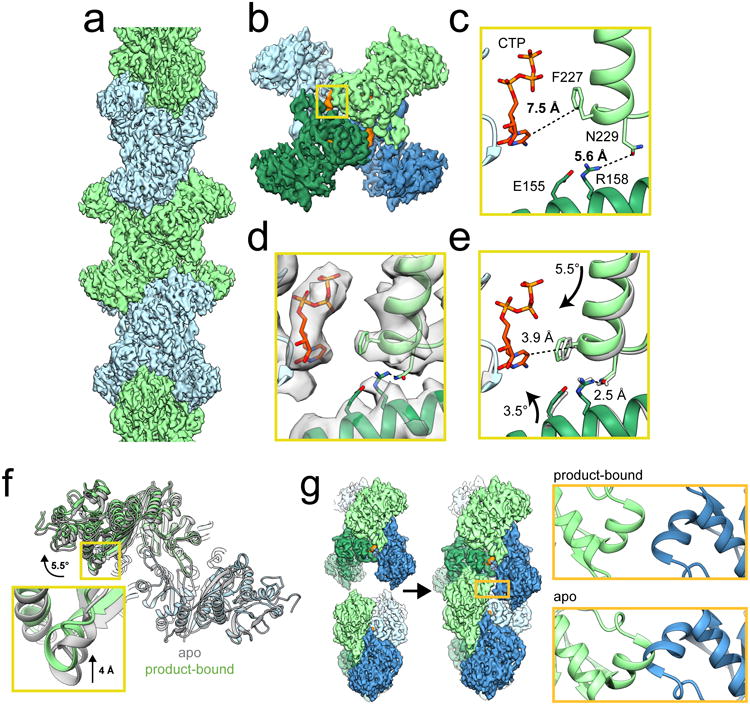
a, CryoEM reconstruction of ecCTPS filament at 4.6 Å resolution. b, A single ecCTPS tetramer from the filament, colored by protomer (blue and green) and nucleotide density highlighted in orange. c, The inhibitory CTP binding site in apo ecCTPS with CTP soaked into the crystals (PDB 2AD5). d, The inhibitory CTP binding site in the cryoEM structure shows compaction of the tetramer around CTP. e, Overlay of the filament structure (gray) with the structure of ecCTPS co-crystallized with CTP (color). Arrows indicate the rotation of subunits relative to the apo conformation in c. f, Overlay of the apo ecCTPS crystal structure (gray) with the CTP-bound filament structure (color). The protomers on the lower right are superposed, revealing a rotation of 5.5° and a 4 Å translation in the positions of the protomers on the upper left. g, Filament assembly contacts between ecCTPS tetramers can only be made in the novel CTP-bound conformation, as superposition of two apo tetramers would result in backbone clashing at the GAT contact site.
