Figure 3. hCTPS1 filaments assemble with substrates and are catalytically active.
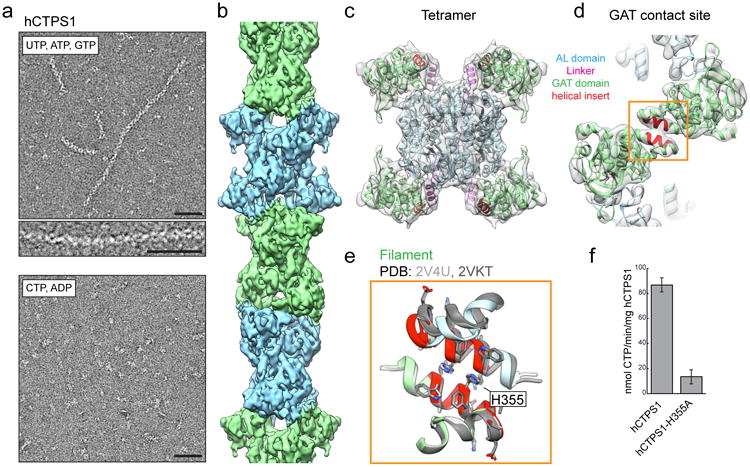
a, hCTPS1 polymerizes in the presence of substrates, but not in the presence of products. b, 6.1Å cryoEM map of the hCTPS1 filament, colored by tetramer subunit. c, Model of the hCTPS1 tetramer fit into the cryoEM map, colored by domain. d, GAT domain contact site in the hCTPS1 filament, with the eukaryotic helical insert shown in red. e, The hCTPS1 filament GAT contact site (color) is also observed in crystal structures of the hCTPS2 GAT domain (grey; PDB 2V4U and 2VKT). f, Wild-type hCTPS1 is more active than the hCTPS1-H355A non-polymerizing mutant. Values are averages of triplicate experiments +/- s.d. Scale bars are 50 nm.
