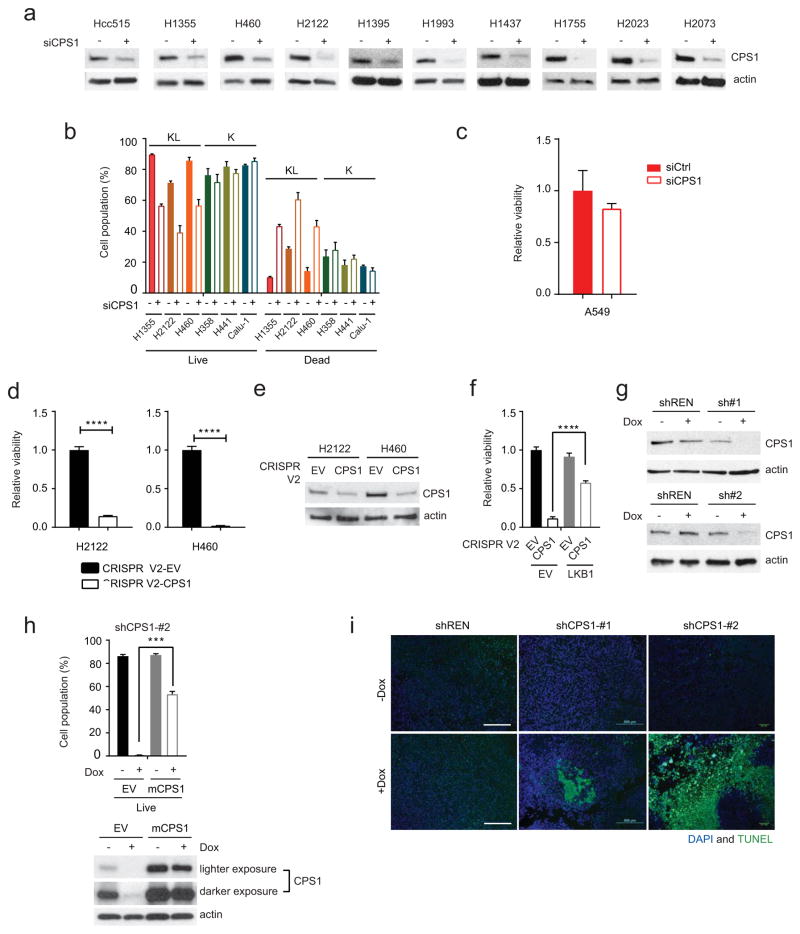
Extended Data Fig. 7. CPS1 addiction in a subset of NSCLC cell lines.
a, Abundance of CPS1 protein in cell lines transfected with a control esiRNA or esiRNA directed against CPS1. b, Effect of CPS1 silencing on cell death in K and KL cells. Data are the average and SD of three independent cultures. c, Effect of CPS1 silencing on A549 cell viability. Data are the average and SD of six independent cultures. d, Effect of lentiCRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of CPS1 on viability in H2122 and H460 cells. Cell TiterGlo assays were performed on pools of CPS1 KO cells without first isolating clones. Data are the average and SD of six independent cultures. e, Abundance of CPS1 protein in H2122 and H460 control cells (EV) and a pool of cells infected with lentiviral CRISPR V2-CPS1 (CPS1). Actin was used as a loading control. f, Effect of knocking out CPS1 on H460-EV and H460-LKB1-WT cells (n=6). g, Abundance of CPS1 in H460 cells expressing shCPS1-#1 (top) and shCPS1-#2 (bottom) with or without Dox induction. shREN is a Dox-inducible control shRNA, and actin was used as a loading control. h, Top, Effects of murine CPS1 (mCPS1) expression on viability in H460 cells expressing shCPS1-#2. Data are the average and SD of three independent cultures. Bottom, Abundance of CPS1 protein in H460 cells expressing mCPS1 with or without shCPS1 induction. Actin was used as a loading control. i, TUNEL staining of tumor tissues. 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) was used to stain DNA. Scale bar, 500 μm. In d, statistical significance was assessed using two-tailed Student’s t-test. ****p<0.0001. In f and h, statistical significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. ***p< 0.001. Tissue TUNEL staining was performed once. Viability assay (f) was performed twice. All other experiments were repeated three times or more.