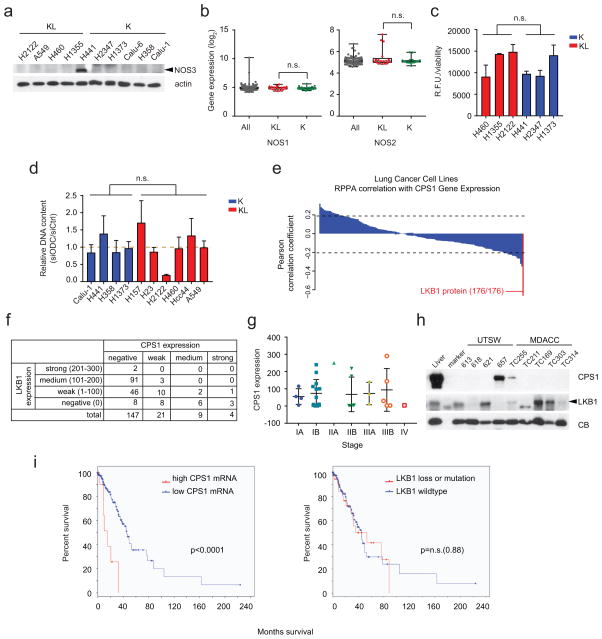
Extended Data Fig. 4. Nitrogen-related metabolic pathways in K and KL cells, and anticorrelation between CPS1 and LKB1.
a, Abundance of NOS3 protein in a panel of K and KL cell lines. b, Distribution of mRNA abundance for NOS1 and NOS2 among 203 cell lines. Complete data sets including quantitative mRNA abundance of these genes are available in Supplementary Information Table 6. c, NOS activity in K and KL cells. Free nitric oxide (NO) was monitored in three cell lines of each genotype. Data are the average and SD of three independent cultures. d, Effect of silencing ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), an enzyme involved in polyamine synthesis from ornithine, in K and KL cells. Cell growth was measured by DNA content using a Perkin Elmer Victor X3 plate reader. Data are the average and SD of six independent cultures. e, Pearson correlation coefficients between CPS1 mRNA and 176 proteins in 94 lung cancer cell lines. Rank of LKB1 protein is indicated. Dashed lines demarcate correlation coefficients at nominal p=0.05. f, Scoring of LKB1 and CPS1 expression in TMA samples. In this analysis, tumors were considered positive if any CPS1 or LKB1 staining was detected (i.e. H-score greater than or equal to 1, as described in Methods); otherwise staining was considered negative. g, CPS1 protein expression in TMA tumor samples of different clinical stages. h, Abundance of CPS1 and LKB1 protein in patient-derived NSCLC xenografts (PDXes). All PDXes had oncogenic KRAS mutations. i, Kaplan-Meier plot associating CPS1 expression with reduced survival. In the TCGA lung adenocarcinoma cohort (TCGA LUAD provisional, n=230), LKB1 mutation or loss was observed in 19% of patient tumors (n=43). For CPS1, a z-score threshold of 2.0 was used to identify tumors with high levels of expression; this included 5.2% (n=12) tumors. There was no difference in overall survival in patients with LKB1 alterations (deletion or mutation) versus those without an LKB1 alteration (p=0.88). In contrast, patients whose tumors had high levels of CPS1 mRNA had much shorter periods of overall survival compared to other patients (15.2 vs. 45.3 months, p<0.0001). The western blot and NOS activity assay were performed twice, and ODC silencing experiment was repeated three times or more. Statistical significance was assessed using two-tailed Student’s t-test. n.s., not significant.