Figure 1.
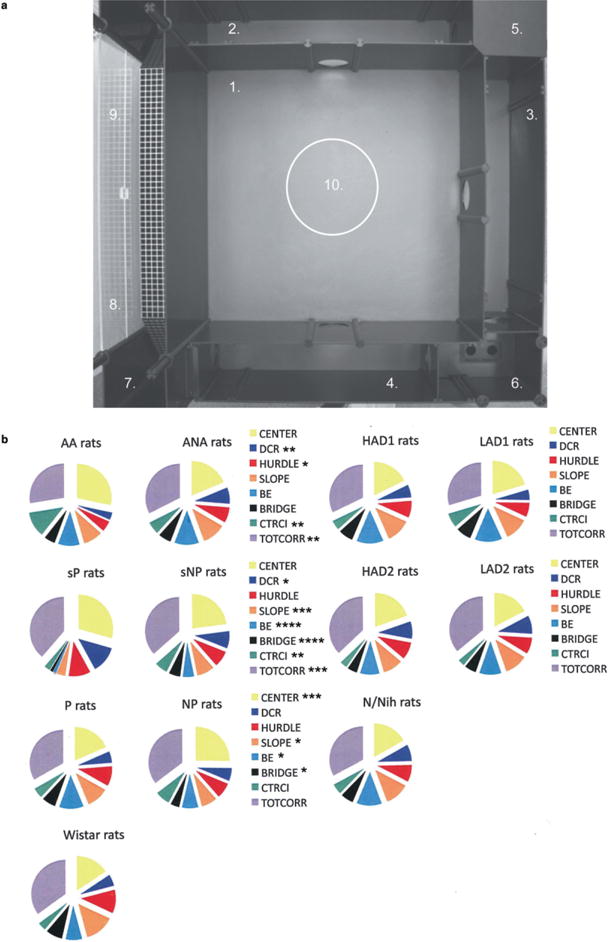
(a) The MCSF arena (100 × 100 cm) and the defined zones (Roman & Colombo 2009) numbered as follows: 1, CENTER, 70 × 70 cm, open area; 2–4, CORRIDORs, transit areas; 5, dark corner room (DCR), area for shelter seeking; 6, HURDLE, high passage to hole board with photocell to count head dips, exploratory incentive; 7, SLOPE, leading up to BRIDGE, risk assessment area; 8, BRIDGE ENTRANCE, risk assessment area; 9, BRIDGE, elevated and illuminated, risk area; 10, CENTRAL CIRCLE, 25 cm diameter, risk area. (b) The percentage number of visits to the CENTER, dark corner room (DCR), HURDLE, SLOPE, BRIDGE ENTRANCE (BE), BRIDGE, CENTRAL CIRCLE (CTRCI) and the CORRIDORs (TOTCORR) in the MCSF test in AA and ANA rats, sP and sNP rats, P and NP rats, all originally related to outbred Wistar rats, and HAD1 and LAD1 rats and HAD2 and LAD2 rats, derived from N/Nih rats. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 comparing the respective alcohol-preferring and non-preferring lines (Mann–Whitney U-test)
