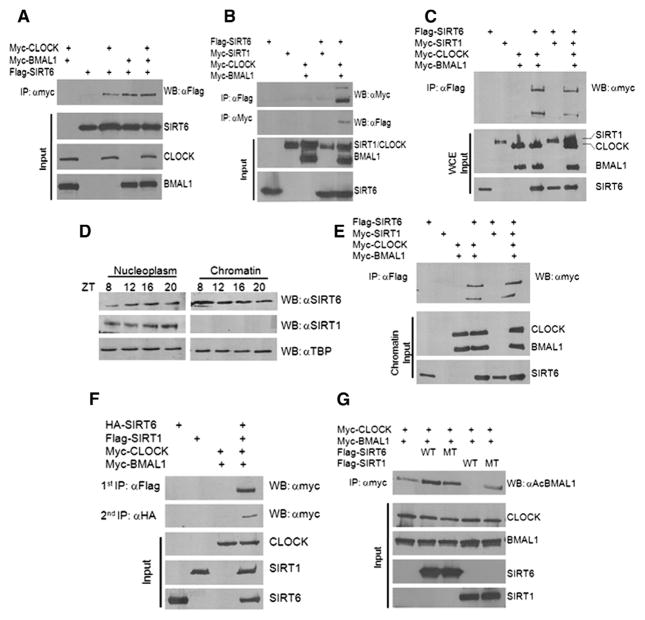
Figure 4. SIRT6, CLOCK, and BMAL1 Interact in an Exclusive Complex from SIRT1.
(A and B) Co-IP experiments were performed in HEK293 cells by ectopically expressing myc-CLOCK, myc-BMAL1, flag-SIRT6, and myc-SIRT1. IP was performed with either anti-myc antibody or Flag-M2 agarose beads overnight, as indicated. Western was performed with anti-myc and anti-flag antibodies as indicated.
(C) myc-CLOCK and myc-BMAL1 were ectopically expressed in HEK293 cells with flag-SIRT6 alone or flag-SIRT6 + myc-SIRT1. Whole-cell extracts (WCEs) were used for Flag IP.
(D) WT liver was fractionated at the indicated ZTs, and nucleoplasmic and chromatin fractions were probed for endogenous SIRT6 and SIRT1 protein expression.
(E) myc-CLOCK and myc-BMAL1 were ectopically expressed in HEK293 cells with flag-SIRT6 alone or flag-SIRT6 + myc-SIRT1. Cells were fractionated and chromatin fraction was used for Flag IP.
(F) Sequential IPs were performed from HEK293 cells ectopically expressing HA-SIRT6, Flag-SIRT1, and myc-CLOCK. Primary IP was performed with Flag (SIRT1), and secondary IP from the same lysates was done with HA (SIRT6) to reveal myc-CLOCK interaction.
(G) BMAL1 acetylation assay was performed in HEK293 cells with ectopic expression of myc-CLOCK, myc-BMAL1, Flag-SIRT6, and Flag-SIRT1 (WT and catalytic mutant). IP was performed with anti-myc and Western with anti-Ac BMAL1 antibody.