Figure 1. Determination of CerS-ACSL5 Association.
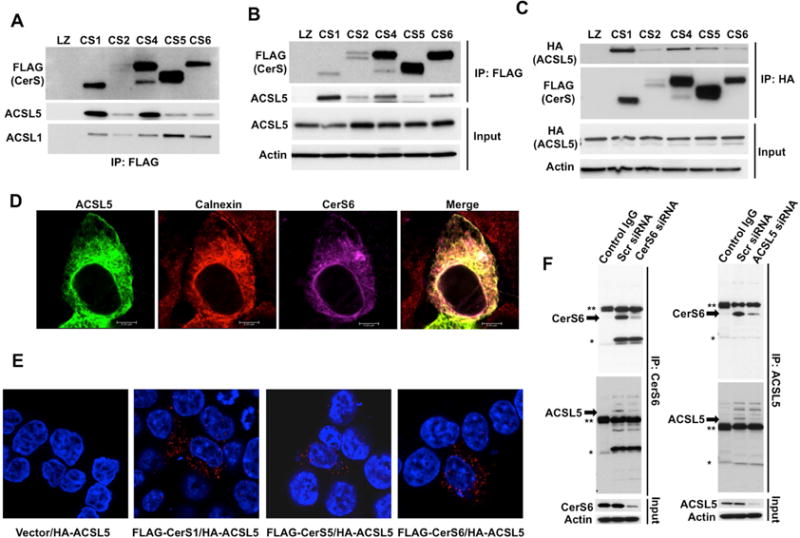
(A) FLAG-tagged CerS1, 2, 4, 5 and 6 were immunoprecipitated after lysis in digitonin containing buffer, and interactions of ACSL1 and ACSL5 with CerS was determined by Western Blotting.
(B) Interactions of ACSL5 and CerS were determined as in A using Triton X-100 containing lysis buffer.
(C) HA-tagged ACSL5 was expressed in cells stably transfected with FLAG-tagged CerS. ACSL5-CerS interaction was determined by Western Blotting with anti-FLAG antibody after immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-HA antibody.
(D) Co-localization of HA-ACSL5 with FLAG-CerS6 and calnexin was imaged by confocal microscopy.
(E) FLAG-tagged CerS and HA-ACSL5 interaction was identified using Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA).
(F) Interaction of endogenous CerS6 with ACSL5 was detected by IP with anti-CerS6 or anti-ACSL5 antibodies followed by Western Blotting after Control (Scr), CerS6, or ACSL5 siRNA transfections. Arrows indicate specific bands. Single and double asterisks indicate light and heavy chains of IP antibodies, respectively. Isotype matched IgG was used as negative control.
Data are representative of three independent experiments.
