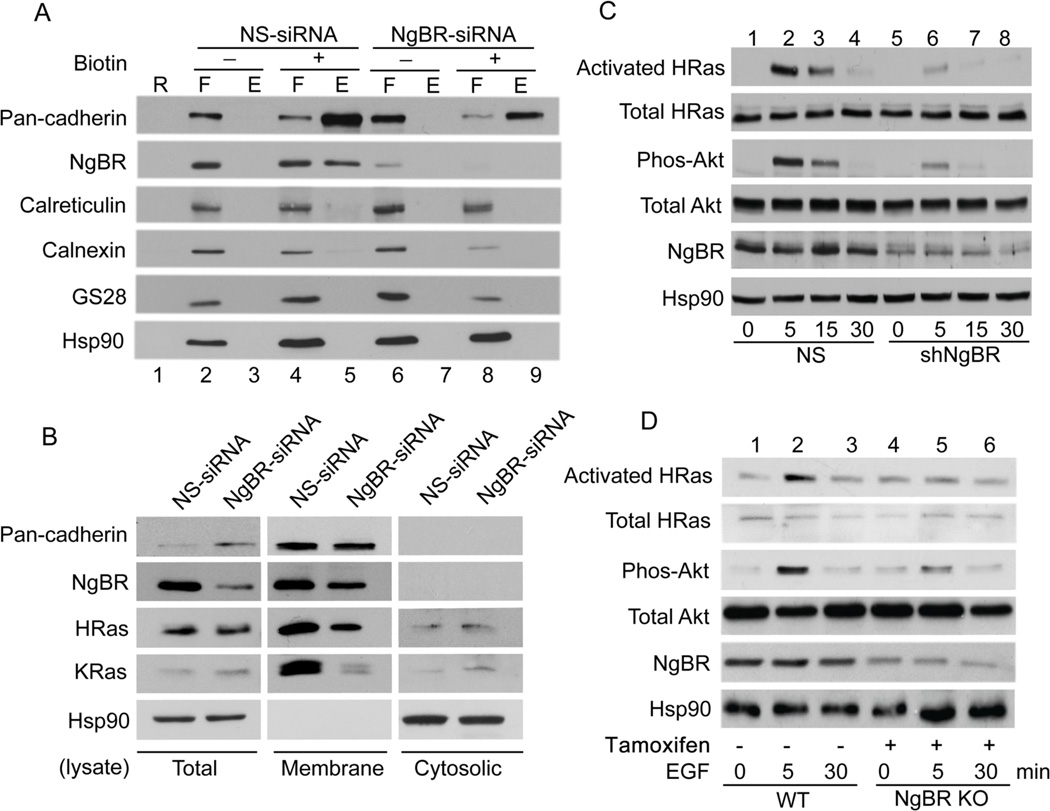
Figure 6. NgBR expression in breast cancer cells is essential for EGF signaling.
(A) Knockdown of NgBR decreases the NgBR protein levels in the fraction of biotinylated cell surface proteins. MDA-MB-231 cell surface proteins were biotinylated under non-permeabilized conditions and isolated using streptavidin agarose resin from Pierce Cell Surface Protein Isolation Kit as described in Figure 1B. Proteins were detected by Western blot analysis. (B) NgBR knockdown diminishes H-Ras and K-Ras membrane localization in MDA-MB-231 cells. NgBR was knocked down by using siRNA. The plasma membrane proteins were isolated by the ultracentrifugation method. The protein levels were determined by Western blotting. (C) NgBR knockdown reduces the EGF-induced activation of H-Ras and phosphorylation of Akt in MDA-MB-231 cells. NgBR was knocked down by using shRNA. The activated Ras proteins were isolated using GST-RBD beads and protein levels were determined by Western blotting. Phosphorylation of Akt and ERK was determined by Western blotting using phosphorylation specific antibodies. (D) NgBR genetic knockout reduces the EGF-induced activation of H-Ras and phosphorylation of Akt in MEF cells. Mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cells were isolated from NgBR inducible knockout mice. NgBR was genetically knocked out by culture with tamoxifen. After stimulation with 10 ng/ml EGF for 5 minutes in the quiescent cells, the activated Ras proteins were isolated using GST-RBD beads. Protein levels were detected by Western blotting. Data are validated in 3 independent experiments.