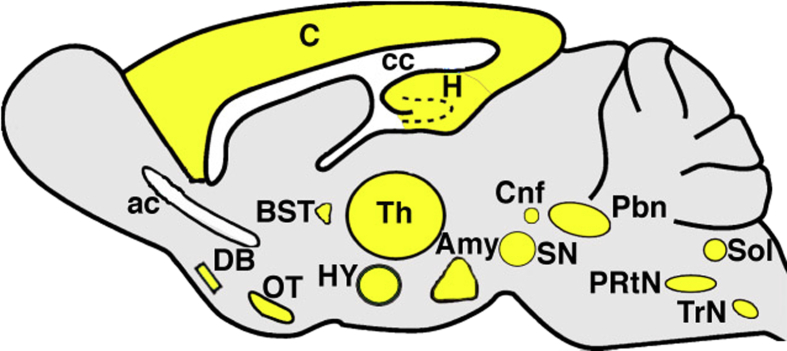
Figure 1.
CFTR in the rat brain. Summary of work by Mulberg et al51, 52 showing CFTR expression (yellow) in the rat brain. Location suggests involvement in energy homeostasis, limbic function, olfaction, motor function, respiration, and autonomic regulation of numerous effector organs, including the airways, GI tract, and heart. Amy = amygdala; ac = anterior commissure; BST = bed nucleus of stria terminalis; C = cortex; cc = corpus callosum; Cnf = cuneiform nucleus; DB = diagonal band of Brocha; H = hippocampus; HY = hypothalamus; OT = olfactory tubercle; Pbn = parabrachial nucleus, PRtN = parvocellular reticular nucleus; Sol = nucleus of the solitary tract; SN = substantia nigra; Th = thalamus; TrN = trigeminal nucleus.