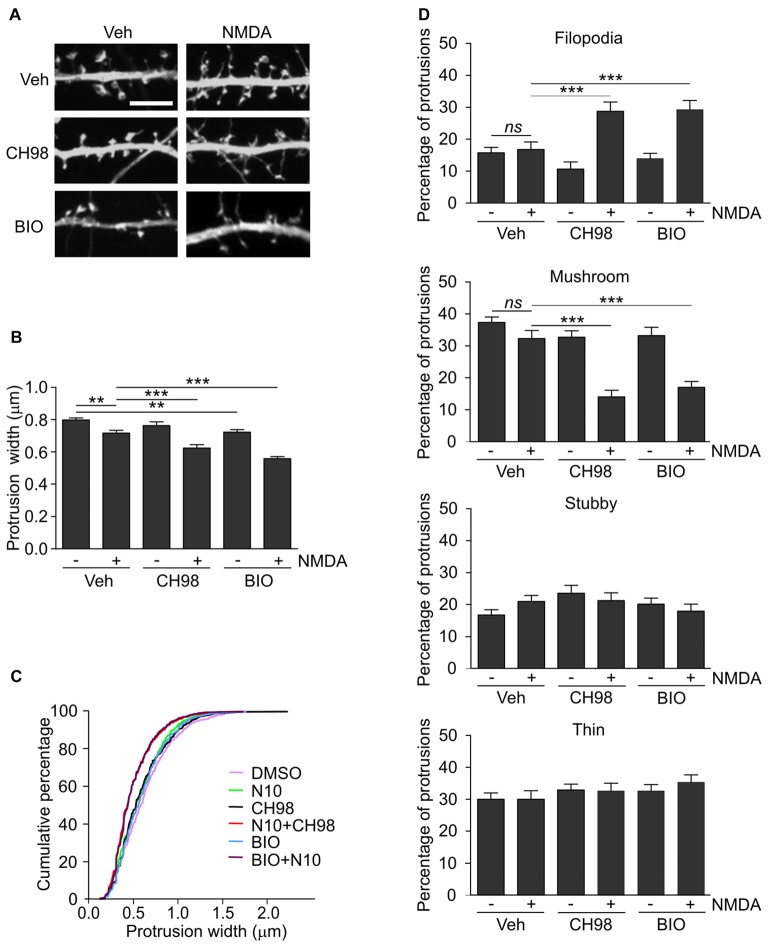
Figure 2.
Combined treatment with NMDA and GSK3α/β inhibitors (CH98, BIO) leads to dendritic protrusion thinning and alterations in dendritic spine morphology. (A) Representative confocal images of dendritic protrusions. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with β-actin-GFP plasmid to visualize cell morphology and stimulated with 10 μM NMDA with or without 1 μM CH98 or 1 μM BIO for 4 h. Scale bar = 5 μm. (B) Quantitative analysis of dendritic spine width. Measurements were averaged per dendrite segment. Two dendrite segments per cell from 10 to 15 cells from two independent cultures were analyzed (5–8 cells per culture). The data are expressed as mean protrusion width ± SEM. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons). (C) Cumulative percentage plot of protrusion width for neurons from (B). Calculations were done for 522–680 spines per condition. (D) Analysis of dendritic protrusion categories for neurons from (B). Categorization was done for dendrite segment and two dendrites per cell were analyzed. Data are expressed as mean percentage of all protrusions ± SEM. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons).