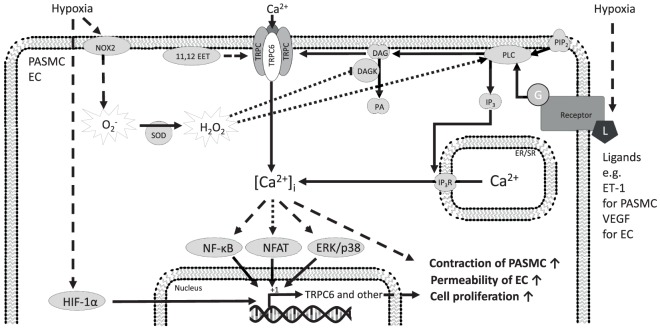
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of TRPC6 regulation and function in precapillary pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) and ECs in response to hypoxia. The TRPC6 protein forms homomeric and heteromeric channels composed of TRPC6 alone or TRPC6 and other TRPC proteins. TRPC6 is expressed in PASMCs from mice, rat, as well as humans and is suggested to play a significant role in human idiopathic PAH. The initiation of TRPC6-mediated Ca2+ influx from the extracellular space is thought to be induced by ligand-activated G-protein coupled receptors, starting a PLC-mediated hydrolyzation of PIP2 to IP3 and DAG. It has been already shown that DAG activates TRPC6-containing channels to induce Ca2+ influx from the extracellular space. Ca2+ entry through TRPC6 might be triggered by hypoxia-induced production or hypoxia-induced DAG accumulation and that the increased [Ca2+]i drives different cellular responses through ERK and p38, NFAT, and NF-κB downstream signaling. These pathways might be involved in the induction of TRPC6 expression and contribute to the modulated cellular response associated with hypoxia. Moreover, hypoxia leads to acute stabilization of HIF-1α, which might induce TRPC6 expression among other proteins. 11,12 EET, 11,12-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid; Ca2+, calcium ion; [Ca2+]i, intracellular Ca2+ concentration; DAG, diacylglycerol; DAGK, DAG kinase; EC, endothelial cell; ER/SR, endoplasmic/sarcoplasmic reticulum; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; ET-1, endothelin-1; G, G-protein; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha; IP3, inositol trisphosphate; IP3R, inositol trisphosphate receptor; L, ligand; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain enhancer of activated B-cells; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T-cells; NOX2, NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) oxidase 2; , superoxide; PA, phosphatidic acid; p38, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; PASMC, precapillary pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PLC, phospholipase C; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TRPC, classical transient receptor potential channel; TRPC6, classical transient receptor potential channel 6; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; solid arrows indicate direct interactions; dotted arrows illustrate indirect interactions. Not all interaction partners have been identified.