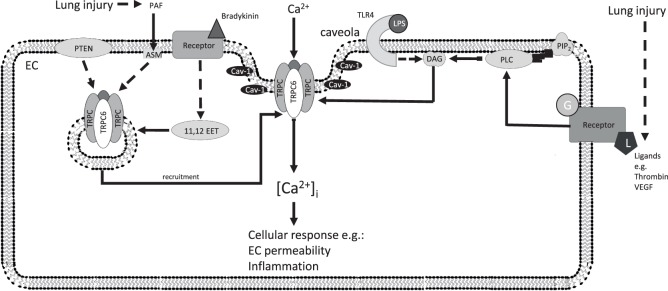
Figure 3.
Additional TRPC6 signaling pathways in ECs after lung injury. Recruitment of TRPC6 by the indicated factors increases the density of TRPC6 channels at the plasma membrane (left), which open after activation of endothelial receptors (right) and increase endothelial permeability and inflammatory processes inducing endothelial dysfunction. 11,12 EET, 11,12-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid; ASM, acid sphingomyelinase; Ca2+, calcium ion; [Ca2+]i, intracellular Ca2+ concentration; Cav-1, caveolin-1; DAG, diacylglycerol; EC, endothelial cell; G, G-protein; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha; L, ligand; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PAF, platelet-activating factor; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PLC, phospholipase C; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; TRPC, classical transient receptor potential channel; TRPC6, classical transient receptor potential channel 6; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; solid arrows indicate direct interactions; dotted arrows illustrate indirect interactions. Not all interaction partners have been identified.