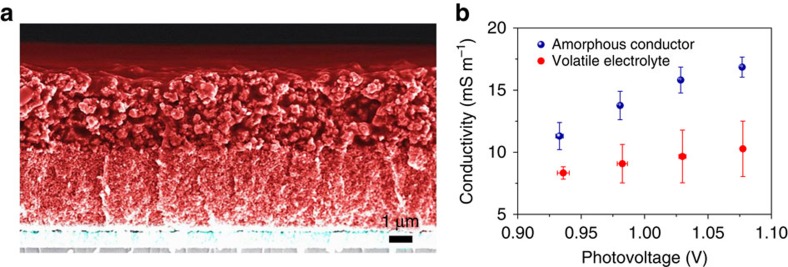
Figure 2. Solid Cu(II/I) hole conductor in solid-state DSCs.
(a) Cross-sectional SEM image of a solid-state DSC without the counter electrode. Moving from the bottom to the top, layers of compact TiO2-coated FTO (cyan), 3.5 μm-thick transparent mesoscopic TiO2+3.0 μm-thick light scattering TiO2 (red), and 2.0 μm-thick solid Cu(I/II) hole conductor overlayer (red) are visible. (b) Photovoltage-dependent conductivity in the solid hole conductor and the volatile electrolyte of solar cells as obtained from the EIS analysis. The solar cells were measured under illumination at 1,000 W m−2 supplied by a white light-emitting diode. The average (symbols) and s.d. (error bars) were calculated from solar cells numbering between four and six.