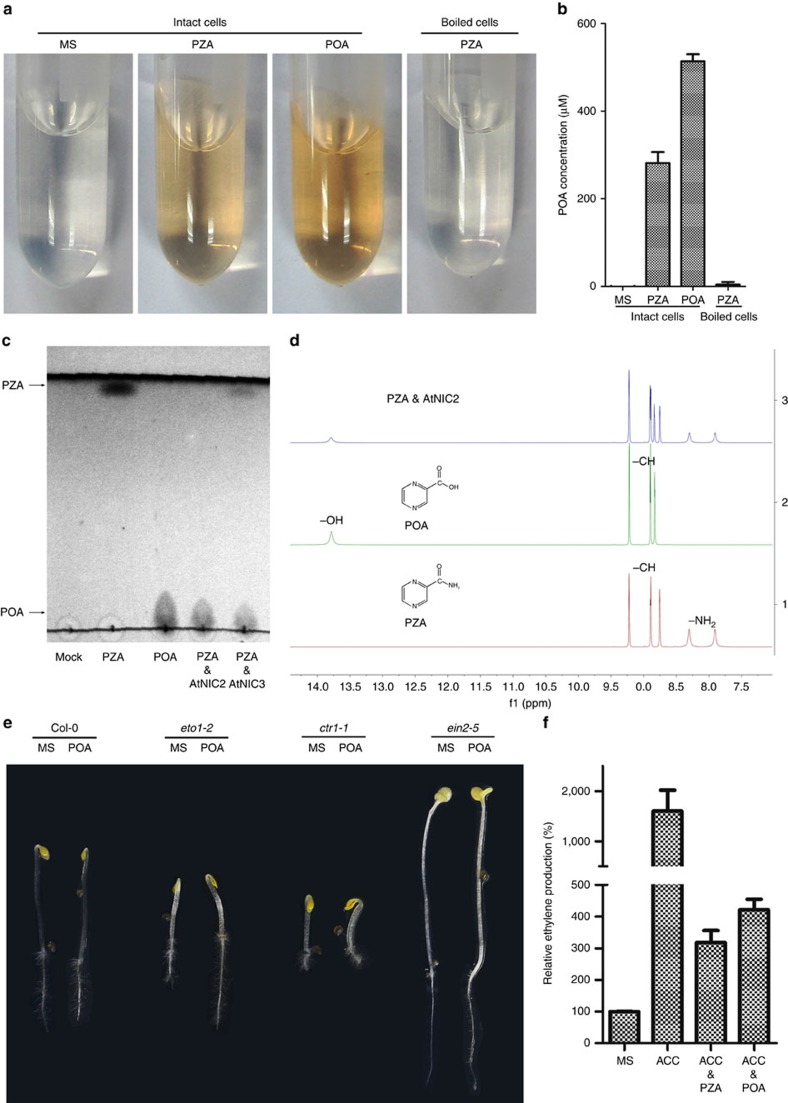
Figure 3. POA is the active form of PZA in Arabidopsis.
(a). The Wayne Test result of PZA application in suspension cultured cells. Cells were cultured in liquid MS or MS medium supplemented with 500 μM PZA or POA for 24 h. The boiled cells with PZA worked as a negative control. (b) Quantification of the POA concentration shown in a. POA concentrations are calculated based on the corresponding 450 nm absorption and the POA-Abs450 standard curve. Bars represent the average concentration (±s.d.) of three independent treatments. (c) TLC (thin layer chromatography) analysis demonstrating that PZA can be hydrolyzed by Arabidopsis NIC2 and NIC3 in vitro. Reaction products were separated by silica TLC plates developing using dichloromethane:methanol (3:1) and detected with ultraviolet. (d) NMR analysis of reaction products of PZA catalyzed by AtNIC2. Products were extracted using ethyl acetate and analysed using Bruker-400 MHz NMR in Dimethyl sulfoxide-d6. The middle panel refers to the POA standard sample whereas the bottom panel is for PZA. The peaks corresponding to the carboxylic acid proton of POA (-OH) and the two amino protons of PZA (-NH2) are denoted. The upper panel indicates the reaction mixture after PZA was treated with AtNIC2, wherein the carboxylic acid proton peak was observed, indicative of the production of POA. (e) 3-day-old etiolated seedlings of Col-0, eto1-2, ctr1-1 and ein2-5 grown on horizontally oriented MS only or MS medium supplemented with 50 μM POA. (f) Quantification of the relative ethylene production (compared to MS treatment) of 3-day-old etiolated seedlings of Col-0 with the application of 100 μM ACC and/or PZA or POA (500 μM) for 24 h. Bars represent the means (±s.d.) of five independent treatments.