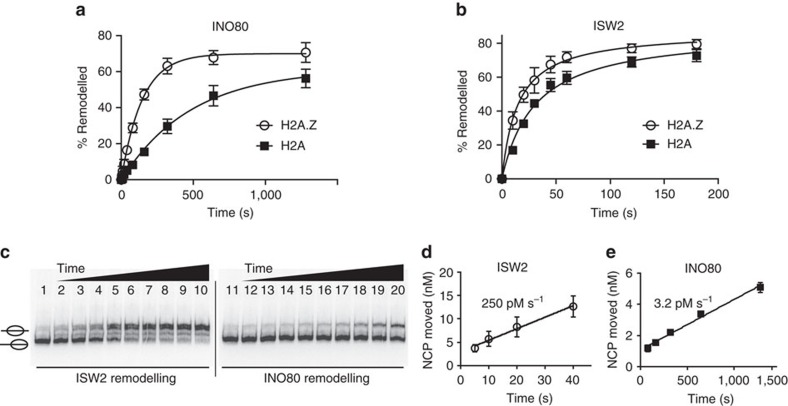
Figure 6. INO80 preferentially mobilizes H2A.Z over H2A nucleosomes.
(a,b) The rates of nucleosome movement by (a) INO80 and (b) ISW2 with H2A.Z and H2A nucleosomes as determined by electrophoretic-mobility shift assay in native gels (Supplementary Fig. 6a). The fractions (%) of nucleosomes moved were plotted versus time to determine the rates of H2A.Z versus H2A nucleosome movement. (c) The efficiencies of ISW2 (lanes 2–10) and INO80 (lanes 11–20) for mobilizing nucleosomes were determined by the rates with which they repositioned H2A-containing nucleosomes. End-positioned (70N0) nucleosomes were completely bound with ISW2 or INO80 and remodelled with 80 μM ATP at 18 °C for 0, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 160, 320, 640 and 1,280s. (d,e) The amounts of nucleosomes moved were plotted versus time to determine the initial rates of nucleosome movement by ISW2 (d) and INO80 (e). NCP is for nucleosome core particles. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean (s.d.) calculated from three technical replicates.