FIG 1.
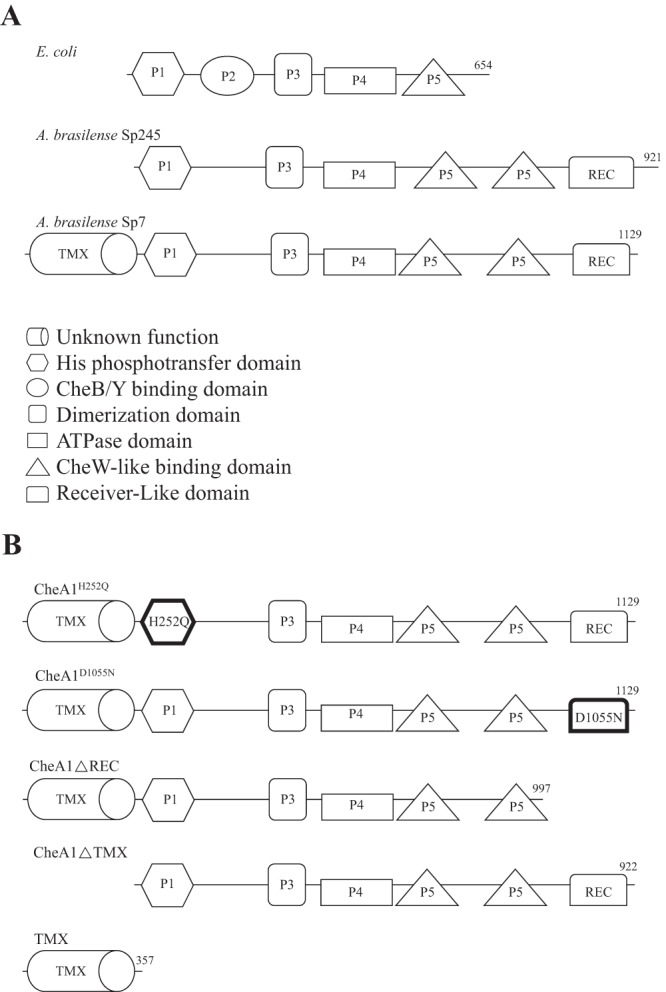
(A) Domain architecture of CheA orthologs in E. coli and A. brasilense strains Sp7 and Sp245. Top, the E. coli CheA contains a histidine phosphotransfer domain which harbors the conserved His residue (P1) followed by a CheB/Y binding domain (P2). The dimerization (dimer) domain (P3) precedes the ATPase domain (P4), which is necessary to phosphorylate the His residue. The binding domain (P5) resides in the C-terminal region. Middle, A. brasilense strain Sp245 CheA1 possesses the P1, P3, P4, and P5 domains and also a receiver-like (REC) domain. Bottom, A. brasilense strain Sp7 CheA1 possesses domains similar to those of strain Sp245, but it also possesses an N-terminal seven-transmembrane region of unknown function (TMX). Numbers at the C termini denote the total number of amino acids present. (B) Schematic representation of A. brasilense strain Sp7 CheA1 variants used in this study. Variants with single-residue replacements (CheA1H252Q and CheA1D1055N) are in boldface.
