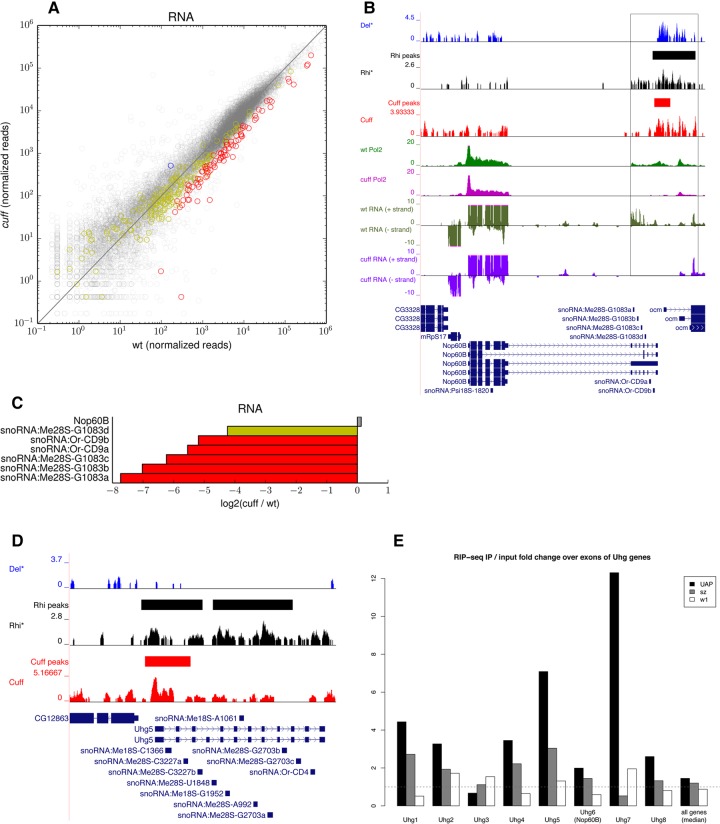
FIGURE 4.
Small nucleolar RNAs are down-regulated in cuff mutant ovaries. (A) Scatter plot displaying the snoRNAs that are up-regulated (blue), down-regulated (red), and not significantly affected (yellow) in the cuff mutant as per RNA-seq. Expression levels of protein-coding genes are displayed in the background (black). Shown on x- and y-axes are consensus normalized read coverage values computed over replicates. (B) Del (blue), Rhi (black), Cuff (red), RNA Pol2 in wild-type (green), and RNA Pol2 in cuff mutant (magenta) ChIP-seq profiles along Nop60B locus. Loci reproducibly bound by Cuff (red) and Rhi (black) are marked with solid lines in separate tracks (not reported for Del due to lack of biological replicates). RNA-seq profiles in wild-type (dark green) and cuff mutant (purple) are also shown. Black frame box highlights the snoRNA cluster in the Nop60B 3′UTR and downstream region that is bound by the RDC complex components. (C) Barplot of the fold difference between wild-type and cuff ovaries for the Nop60B coding region and for the snoRNAs hosted within its 3′UTR as per RNA-seq [log2 (cuff/wt)]. (D) Del (blue), Rhi (black), and Cuff (red) ChIP-seq profiles along the Uhg5 gene. Regions reproducibly bound by Cuff (red) and Rhi (black) as per ChIP-seq are marked with solid lines. (E) UAP56 RIP-seq at Uhg transcripts. Barplot shows the fold enrichment of the RIP-seq signal over corresponding input for the exons of the Uhg genes. Barplot for the wild-type UAP56 (UAP), the mutated UAP56sz15″ variant (sz), and for the control (w1) are shown. Only the last seven exons were used for Uhg6 (Nop60B), and only exons not overlapping the RpL23A locus were used for Uhg7, to avoid contamination from protein-coding sequence. Median of the values for all genes is shown in the last column. This analysis was performed based on data sets from Zhang et al. (2012).