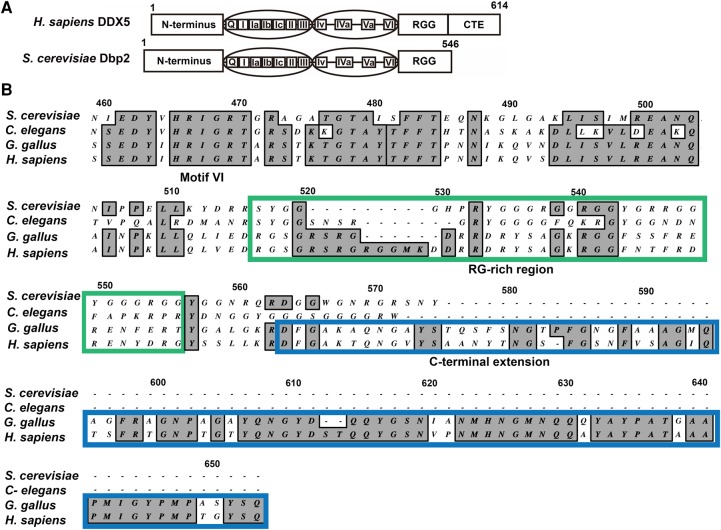
FIGURE 1.
DDX5/Dbp2 orthologs share common DEAD-box core motifs but differ at the carboxy termini. (A) Schematic of human DDX5 and S. cerevisiae Dbp2 proteins. The amino terminus, 12 DEAD-box protein motifs, and RG-rich (or RGG) region are conserved. DDX5 has a carboxy-terminal extension (CTE) that is not conserved with Dbp2. DDX5 and Dbp2 protein sequences have 55% identity and 70% similarity. (B) The CTE is specific to mammalian/avian DDX5. Amino acid alignment of the carboxy terminal ends of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Dbp2 (NP_014287), Caenorhabditis elegans DDX17 (NP_001041134), Gallus gallus DDX5 (NP_990158), and Homo sapiens DDX5 (NP_004387), from motif VI through the CTE. Multiple sequence alignment was performed using the ClustalW alignment tool (Thompson et al. 1994) with 40 open gap penalty in MacVector 11.1.2. Numbers correspond to the alignment, not the amino acid sequences of Dbp2/DDX5. The RG-rich region is highlighted with a green box. The CTE of DDX5 is marked with a blue box.