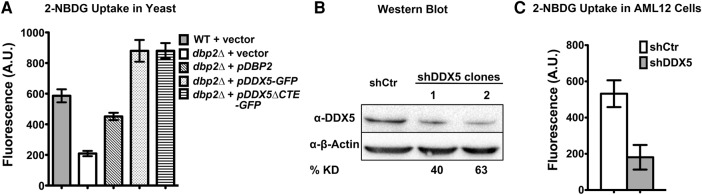
FIGURE 6.
Both Dbp2 and DDX5 promote glucose import in S. cerevisiae and mammalian cells, respectively. (A) Ectopic expression of DDX5 or DDX5ΔCTE rescues glucose import defects in dbp2Δ cells. Glucose import was determined using 2-(N-(7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl)amino)-2-deoxyglucose (2-NBDG) uptake assays (Blodgett et al. 2011), which measure the fluorescence intensity of 2-NBDG in cells after lysis. A.U., arbitrary units. Data show the mean ± SD of three independent biological replicates. (B) Western blots show shRNA knockdown levels of DDX5 in mouse hepatocytes (AML12). Western blotting of DDX5 or β-actin was performed from cell lysates from two independent AML12 clones stably expressing a shRNA targeting DDX5 (shDDX5) or a nontargeting control shRNA (shCtr). The percent of knockdown of DDX5 was quantified by densitometry relative to β-actin loading control. (C) DDX5 promotes glucose uptake in AML12 cells. 2-NBDG uptake assays in mouse AML12 cells expressing shDDX5 or shCtr. Cells were incubated at 37°C with fully supplemented culture media containing 100 µM 2-NBDG for 30 min. 2-NBDG uptake was measured as above.