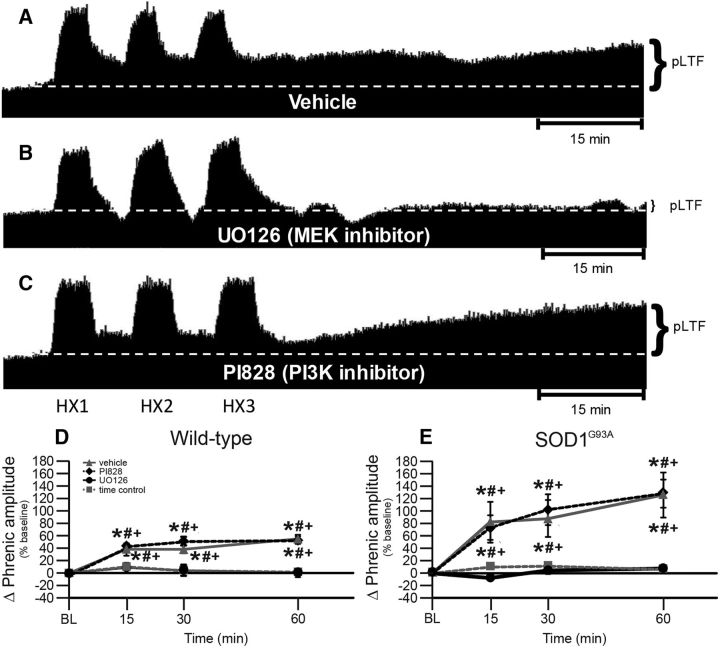
Figure 4.
pLTF in UO126-treated and PI828-treated rats. A–C, Representative traces of compressed, integrated phrenic nerve activity before and after AIH in end-stage SOD1G93A rats pretreated with vehicle (A), UO126 (B), or PI828 (C). White dashed line in each trace indicates baseline. AIH elicits pLTF in vehicle-pretreated and PI828-pretreated rats, but was nearly abolished in UO126-pretreated rats. D, E, Phrenic burst amplitude (percentage change from baseline) in wild-type (D) and SOD1G93A (E) rats pretreated with vehicle (gray triangles with gray solid line), PI828 (black diamonds with black dashed line), or UO126 (black circles with black solid line), or TCs (gray squares with gray dashed line). pLTF is increased in wild-type and SOD1G93A rats treated with vehicle or PI828 compared with baseline (+) and with TCs (*). Wild-type and SOD1G93A rats treated with UO126 had a significantly smaller pLTF compared with vehicle or with PI828 (#). Values are means ± 1 SEM; significant differences are p < 0.05.