Figure 1.
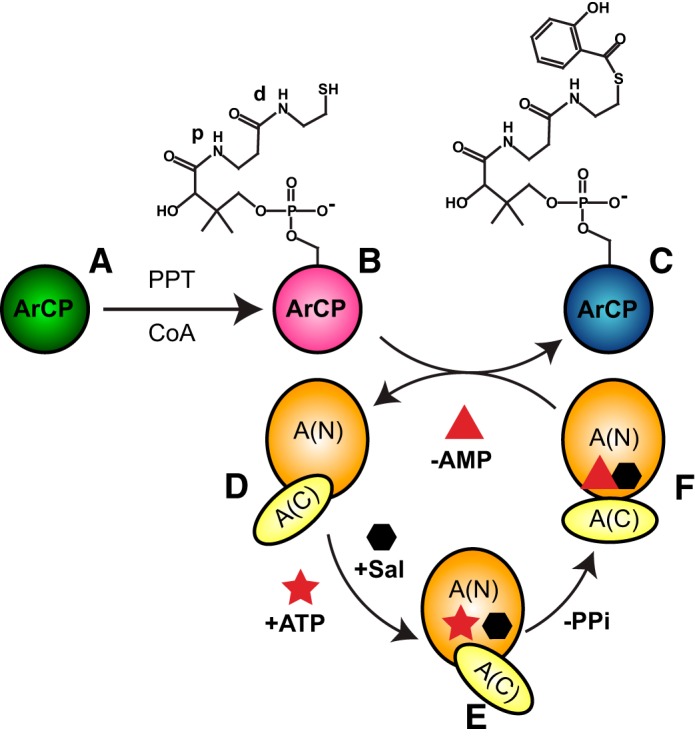
Covalent modifications of the yersiniabactin synthetase ArCP during NRPS synthesis. A PP transferase (PPT) converts apo-ArCP (A) to holo-ArCP (B) upon attachment of PP to Ser52. An adenylation domain loads salicylate (hexagon) on holo-ArCP (C). This A-domain first adopts an adenylation conformation (E) to activate the substrate through ATP (star) into a high-energy adenylate, SalAMP, where AMP is represented as a triangle. Next, a thioester conformation (F) allows for tethering the substrate to holo-CP with release of AMP. A third conformation may exist for the free domain (D). The proximal and distal amide groups in PP, discussed in the legend to Fig. 5, are labeled with p and d, respectively.
