Figure 10.
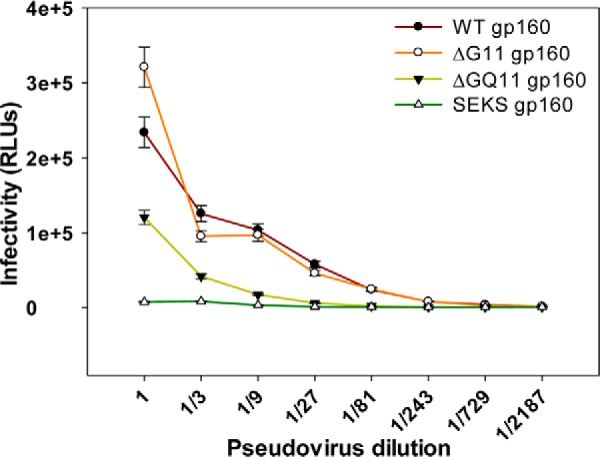
Effect of rationally designed versus conventional Asn → Gln glycosylation site mutations on pseudoviral infectivity. Infectivity of pseudoviruses containing WT or differentially glycosylated JRFL gp160 Env was measured using a TZM-bl assay. The relative amount of pseudotyped virus in cell supernatants was normalized following a p24 assay, and equal amounts of each pseudovirus were used for the infectivity assay. Pseudoviruses with ΔG11 gp160 Env retain WT-like infectivity, and pseudoviruses displaying ΔGQ11 gp160 show a drastic reduction in infectivity. As expected, pseudoviruses incorporating cleavage-defective SEKS gp160 Env show loss of infectivity because they lack a properly cleaved, native-like trimeric envelope. Error bars represent standard deviation for the data from two independent experiments. RLUs, relative luminescence units.
