Figure 2.
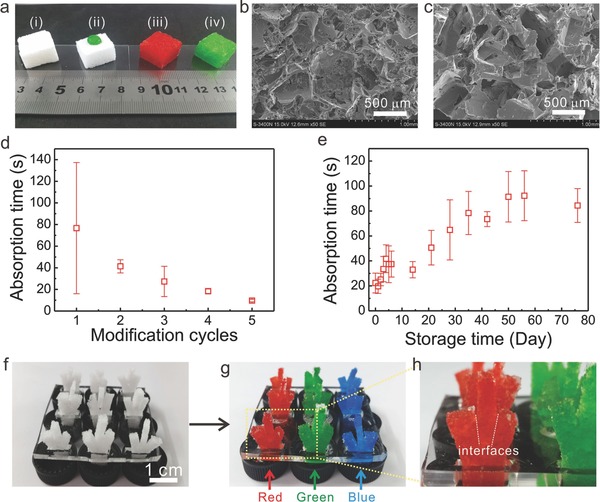
a‐i) Digital images of the original sugar cube, ii) PDMS sponge with one drop of green food dye solution on the top surface, iii) air‐plasma treated PDMS sponge absorbed with red food dye solution, and iv) PVA‐PDMS sponge absorbed with green food dye solution. SEM images of the as‐made PDMS sponges b) before and c) after surface modification with PVA solution. d) Relationship between the wettability (represented by the time for absorbing a 2 µL water droplet) and “dip‐coat‐dry” modification cycles. e) Hydrophilic stability test of the PVA modified PDMS sponges. Photograph of arrays of artificial trees made of the PVA‐PDMS sponges f) before and g) after absorption with food dye aqueous solutions. h) Magnified photograph of an artificial tree showing the interfaces between different sponges.
