Figure 2.
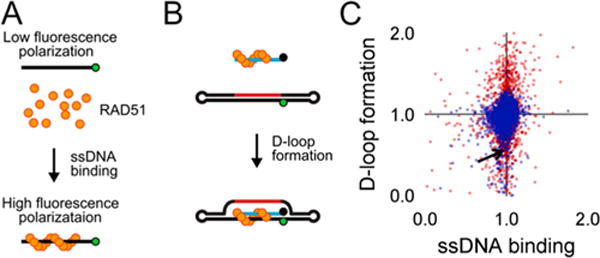
High-throughput (HT) screen for compounds that inhibit RAD51’s D-loop activity. (A) One biochemical assay monitors RAD51 binding to fluorescently labeled ssDNA, which is detected as an increase in fluorescence polarization. (B) A second parallel biochemical assay monitors fluorescence intensity, which decreases upon pairing of Black Hole Quencher 1-labeled ssDNA with a fluorescein-labeled complementary double-hairpin duplex. (C) Compounds were tested for the ability to influence the efficiency of these two RAD51-mediated processes, and the results of this HT are displayed. Blue symbols = ASDI library compounds, red symbols = LOPAC library compounds. Arrow indicates the position of compound 1.
