Figure 7.
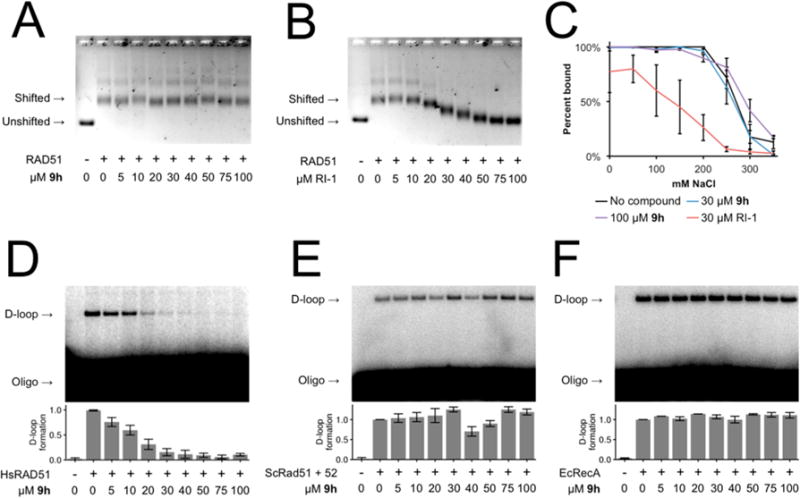
(A,B) Electromobility shift assay showing RAD51-ssDNA binding in the presence of 9h or RI-1, respectively. (C) 9h does not destabilize RAD51-ssDNA nucleoprotein filaments as shown by salt titration midpoint. RI-1 serves as a positive control for disruption of RAD51-ssDNA nucleoprotein filament stability. Error bars denote the standard error for three replicates. (D,E,F) Representative D-loop assay gel images showing recombinase-mediated assimilation of a radiolabeled ssDNA oligonucleotide into the homologous region of a supercoiled dsDNA plasmid in the presence of 9h by human RAD51 protein, S. cerevisiae Rad51 and Rad52 proteins, or E. coli RecA protein, respectively. Error bars denote the standard error for three replicates.
