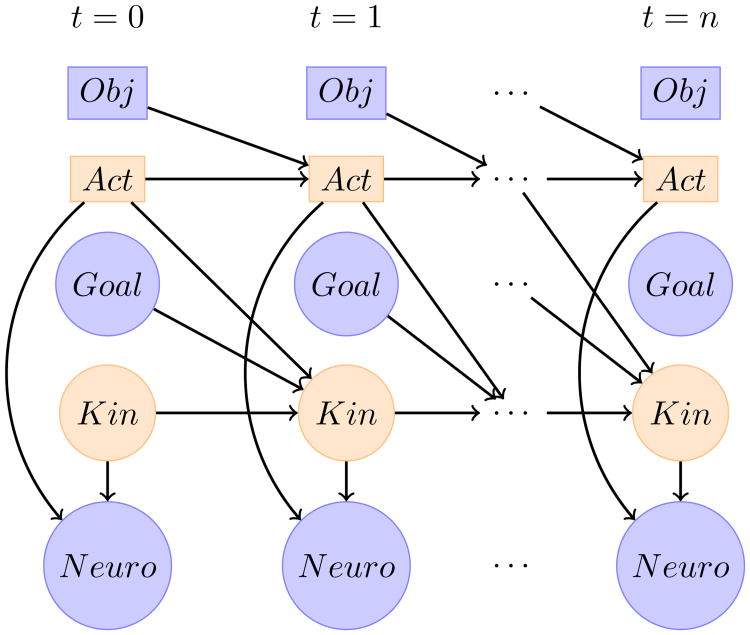
Figure 1.
Dynamic Bayesian network of motion prediction using computer vision and neural signals. Rectangles represent categorical (discrete) variables, circles are continuous. Blue is observed, and orange is inferred at each time step. Obj represents the type of selected object (possibly none), Act is the desired action to execute (e.g. rest or drink), Goal is the 3D endpoint the user is trying to reach, Kin is the current 3D position, velocity, and acceleration, and Neuro is the feature vector extracted from the neurological signals. Arrows denote conditional dependencies between variables.