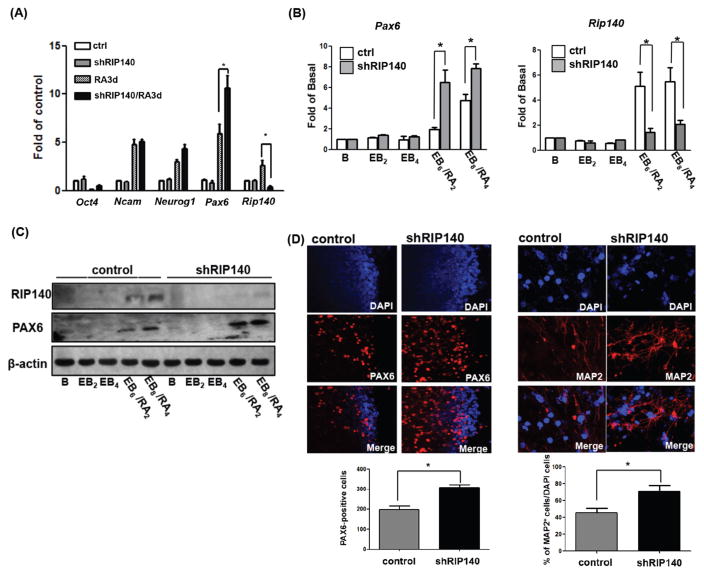
Figure 1.
Silencing RIP140 increases MAP2- and PAX6-positive cells under retinoic acid (RA) induced differentiation. Expression during RA-induced (A) or embryoid body (EB)/RA-induced (B) differentiation of control embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and shRIP140 ESC clones, as detected by q-PCR. Embryoid body differentiation kinetics denoted as follows: B, unstimulated ESC; EB2, 2 days embryoid body; EB4, 4 days embryoid body, EB6/RA2 6 days embryoid body with 2 days RA treatment, and EB8/RA4 8 days embryoid body with 4 days RA treatment. (C): Western blot analyses of RIP140, PAX6, and β-actin in EB/RA-induced differentiation. (D): Immunofluorescence images of differentiated ESCs (EB8/RA4) stained with PAX6 (left panel). PAX6-positive cells were quantified from scoring seven random areas (left bottom). Neurons differentiated from control EBs or shRIP140 EBs were stained with neuronal marker MAP2 (right panel), and nuclei were visualized by DAPI staining. Total cells (DAPI+) and MAP2-positive neurons in five randomly selected areas were scored to determine the frequency of neuron production (n = 3 or more) (right bottom panel). Asterisks denote a statistically significant difference (p < .05).