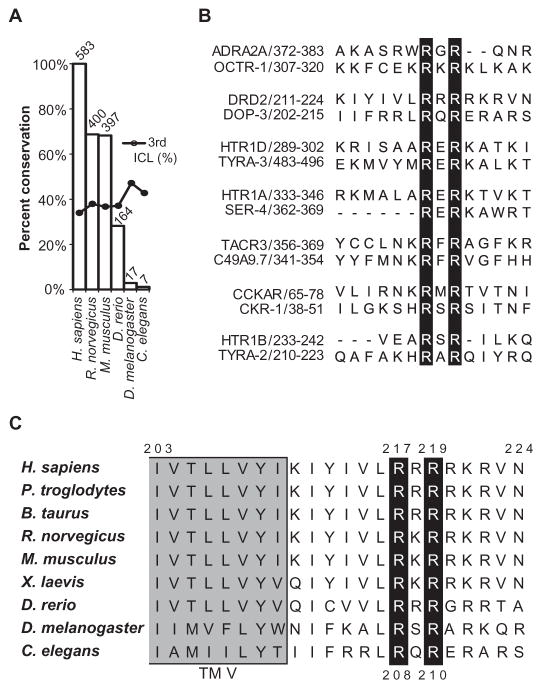
Fig. 1. Predicated methylation motifs within the intracellular domains of GPCRs.
(A) Plot indicating the conservation of arginine methylation motifs across species. Among 737 annotated human GPCRs in the NCBI HomoloGene database, 300 contain a total of 583 predicted arginine methylation motifs (RGG or RXR). The height of each bar represents the percentage conservation of these sites between the human receptors and their homologs in the indicated species, and the number above each bar indicates the total number of predicted motifs conserved in each species. Dots indicate the percentage of motifs that are located within the third intracellular loop (ICL). (B) Alignments indicating conservation of the seven human and C. elegans GPCRs that contain conserved predicted arginine methylation motifs, as generated with the MUSCLE (multiple sequence comparison by log-expectation) algorithm (48). The human GPCR sequences are on top, and the corresponding C. elegans receptor sequences are aligned below. Amino acid positions are indicated after the receptor names. Black bars highlight the conserved arginine residues. (C) Alignment indicating conservation of residues among the D2 receptor homologs. The Arg217 and Arg219 residues of the human D2 receptor and their counterparts in other species lie within a highly conserved RXR motif, in which X can be any amino acid residue. These arginines are conserved from the C. elegans D2-like dopamine receptor DOP-3 to the human D2 receptor. The gray shading indicates the end of transmembrane domain five (TM V).