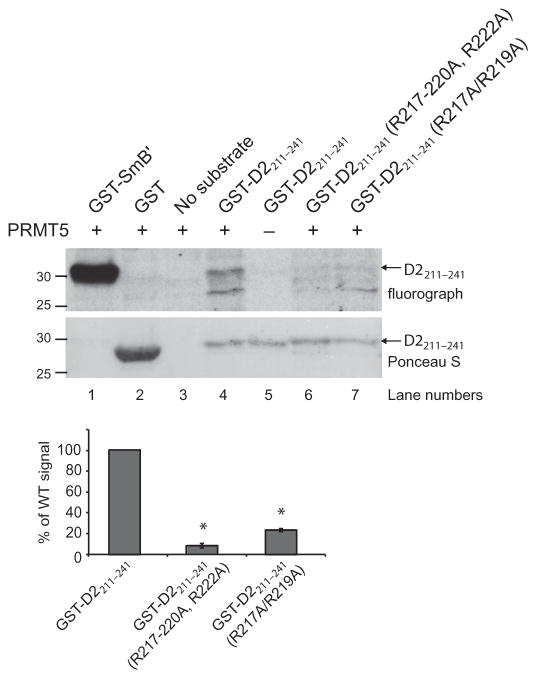
Fig. 2. PRMT5 methylates the human D2 receptor in vitro.
The indicated GST-tagged wild-type (WT) and mutant recombinant fragments of the third intracellular loop (amino acid residues 211 to 241) of the human D2 receptor were used in an in vitro methylation assay with active recombinant human PRMT5 as described in Materials and Methods. The PRMT5 substrate GST-SmB′ was used as a positive control, whereas GST alone served as a negative control. Top: Fluorograph shows that the WT GST-D2211–241 fragment was methylated in a PRMT5-dependent manner. The degrees of methylation of GST-D2211–241(R217–220A, R222A) and GST-D2211–241(R217A/R219A) were 10 and 24%, respectively, of that of the WT fragment. Ponceau S staining of the polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane was performed to demonstrate equivalent loading of receptor fragments. Molecular mass markers (kD) are indicated on the left. Bottom: Quantification of the degree of methylation of the receptor fragments based on densitometric analysis of fluorographs. Data are means ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P = 0.000001.