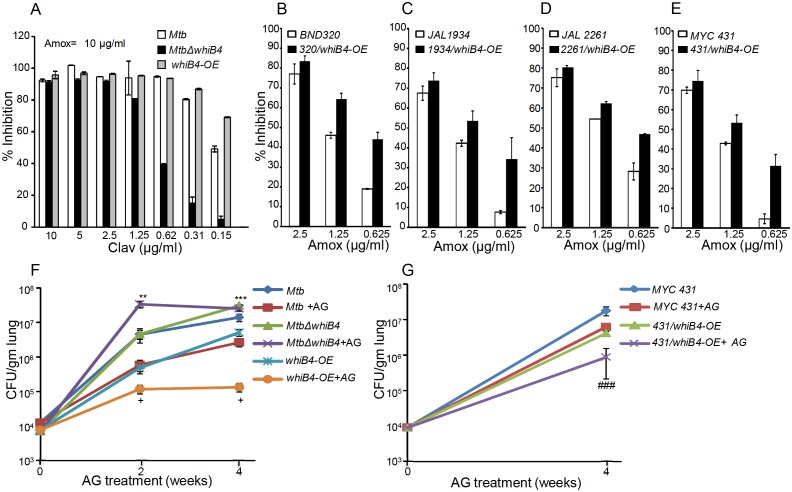
Figure 9. WhiB4 regulates AG tolerance in drug-sensitive and -resistant strains of Mtb.
(A) Wt Mtb, MtbΔwhiB4 and whiB4-OE were incubated with Amox (10 µg/ml) and different concentrations of Clav and % inhibition of growth was measured by AB assay as described in Materials and methods. To determine if WhiB4 modulates the sensitivity of AG in drug-resistant strains, WhiB4 was over-expressed in clinical strains (B) BND 320 (C) JAL 1934, (D) JAL 2261, and (E) MYC 431. Cells were incubated with Clav (8 µg/ml) and different concentrations of Amox. The percent growth inhibition was measured by AB assay as described in Materials and methods. WhiB4 modulates susceptibility to AG during acute infection in mice (F–G). Inbred BALB/c mice (n = 3) were given various strains of Mtb in the form of an aerosol and orally administered with Amox (200 mg/kg of body weight) and Clav (50 mg/kg of body weight) that is AG twice a day starting from day 3 post-infection. Bacterial burden in the lungs was assessed by checking the survival of Mtb strains using CFU analysis. Statistical significance for the pulmonic bacterial load was obtained as follows: by comparing the CFU obtained from AG-treated Wt Mtb and MtbΔwhiB4 strains: **p≤0.01 and ***p≤0.001, by comparing CFU obtained from AG-treated Wt Mtb and whiB4-OE strains: + p≤0.05, by comparing CFU obtained from AG-treated MYC 431 and MYC 431/whiB4-OE strains: ### p≤0.001.