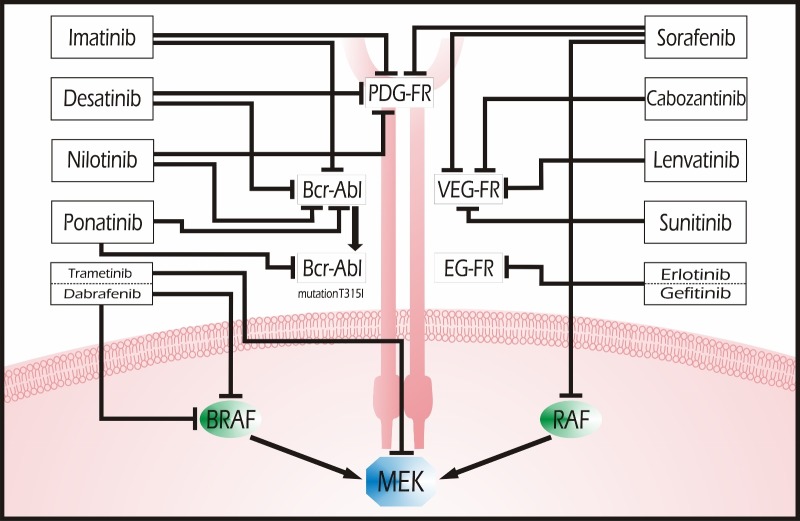
Figure 1. Small Molecule Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors.
The overexpression and/or mutation of tyrosine kinase signaling proteins has been shown to cause abnormal cell proliferation and differentiation, angiogenesis, and inhibition of apoptosis. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are small molecules that inhibit phosphorylation and, hence, activation of kinases by targeting them at the receptor or intracellular level. Since tyrosine kinases are ubiquitous in distribution, TKIs can adversely affect multiple organs, including the heart. Figure 1 shows the activity of each inhibitor drug on the different kinases.