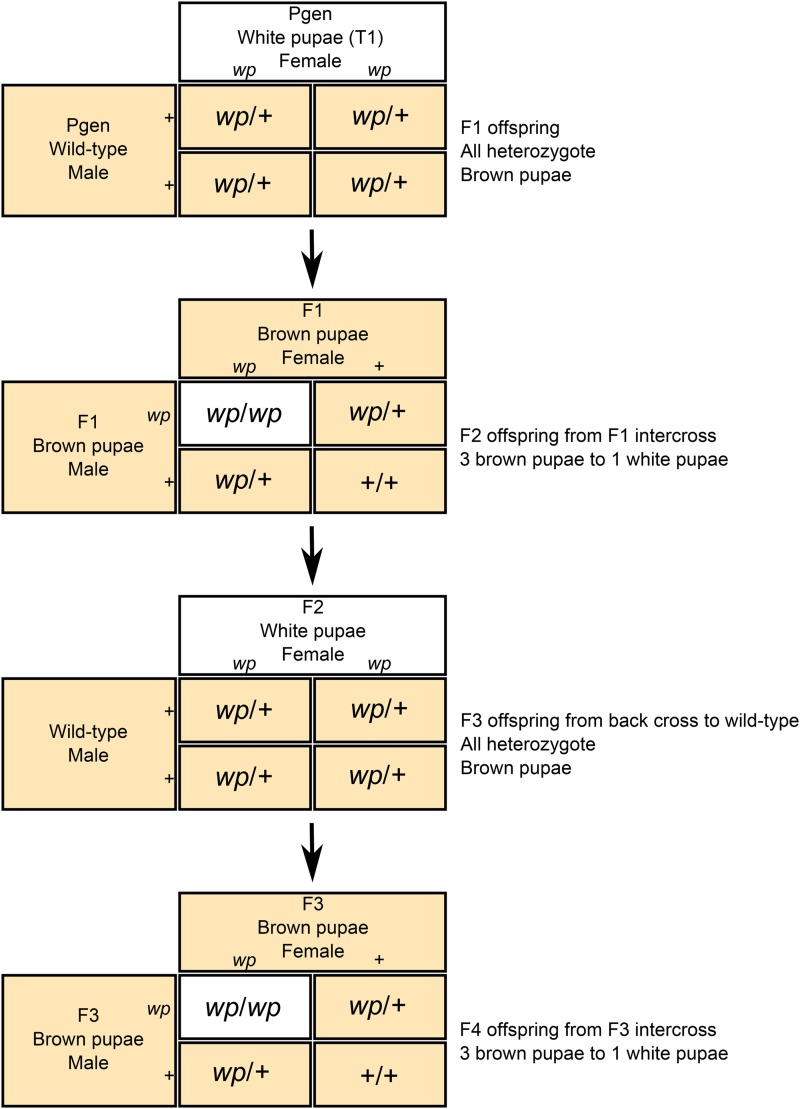
Figure 3.
Crossing scheme used to generate F4 mapping population. Virgin adult females from the B. cucurbitae white pupae genetic sexing strain were mated in isolation with males from the wild-type laboratory colony. The white pupae trait is autosomal recessive; resulting F1 progeny will all have a wild-type brown pupal color phenotype. In F2 progeny from isolated intercrossing between F1 full sibs, the pupal color phenotype will segregate at a 3:1 ratio of wild-type brown pupae to white pupae. White pupae F2 females were backcrossed to wild-type laboratory colony males. This increases the proportion of the wild-type alleles genome in subsequent offspring. Like the F1 progeny, the F3 progeny will all have a wild-type brown pupal color phenotype and full sibs will be intercrossed to produce an F4 mapping population comprised of female and male wild-type brown pupae and white pupae individuals.