Figure 8.
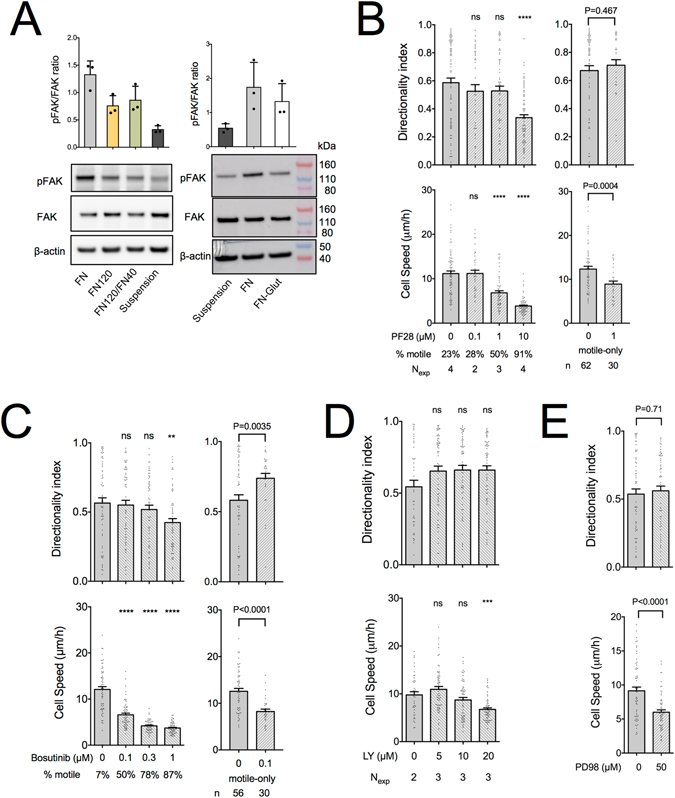
Cell speed and directional persistence in fibroblast migration are differentially regulated. (A) Western blot analysis of phosphorylated (Y397) and total FAK from REF lysates, prepared from cells seeded on indicated substrates for 30 minutes. Quantification through densitometry (Nexp = 3) revealed higher pFAKY397 levels on FN compared to FN120, FN120/FN40 and FN-Glut. Mean ± s.d. are presented. (B) REF speed and directionality index on FN in presence of the FAK inhibitor PF-573228 (PF28). 1 μM PF28 significantly reduced cell speed but did not affect directional persistence. At 10 μM, cells did not translocate, but the nucleus still wiggled within the cell body, giving rise to a low speed and directionality index. The percentage of motile cells (cells exhibiting a maximum displacement of >50 μm from the point of origin at any time during the observation period) and the number of independent experiments are indicated on the graph. When motile-only cells were analyzed, a non-significant increase in directionality index was observed for cells treated with 1 μM PF28 compared to controls (unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction). (C) REF speed and directionality index on FN in presence of the c-Src inhibitor Bosutinib revealed similar results to FAK inhibition. At concentrations of 0.1 and 0.3 μM, Bosutinib significantly reduced cell speed but did not affect directional persistence. The percentage of motile cells is indicated on the graph (Nexp = 3; n = 60). Directionality index for motile-only cells was significantly higher for 0.1 μM Bosutinib compared to controls (unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction). (D) REF speed and directionality index on FN in presence of the PI3K inhibitor LY294,002 (LY). PI3K inhibition resulted in a reduction of cell speed at 20 μM, and a small, non-significant increase in directionality index. (E) REF speed and directionality index on FN in presence of the MEK inhibitor PD98059 (PD98). Inhibition of the ERK/MAPK pathway resulted in a significant reduction of cell speed but had no effect on directional persistence (Nexp = 3; n = 60). Control conditions (0 μM) in (B–E) correspond to samples with the same amount of DMSO as that used for the highest inhibitor concentration. Values in presence of inhibitors were compared to controls using one-way ANOVA analysis (B–D) or unpaired t-tests (E). Coating concentrations of FN: 10 μg/ml. Mean ± s.e.m. are presented. ns: not significant; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
